GS Paper III
News Excerpt:
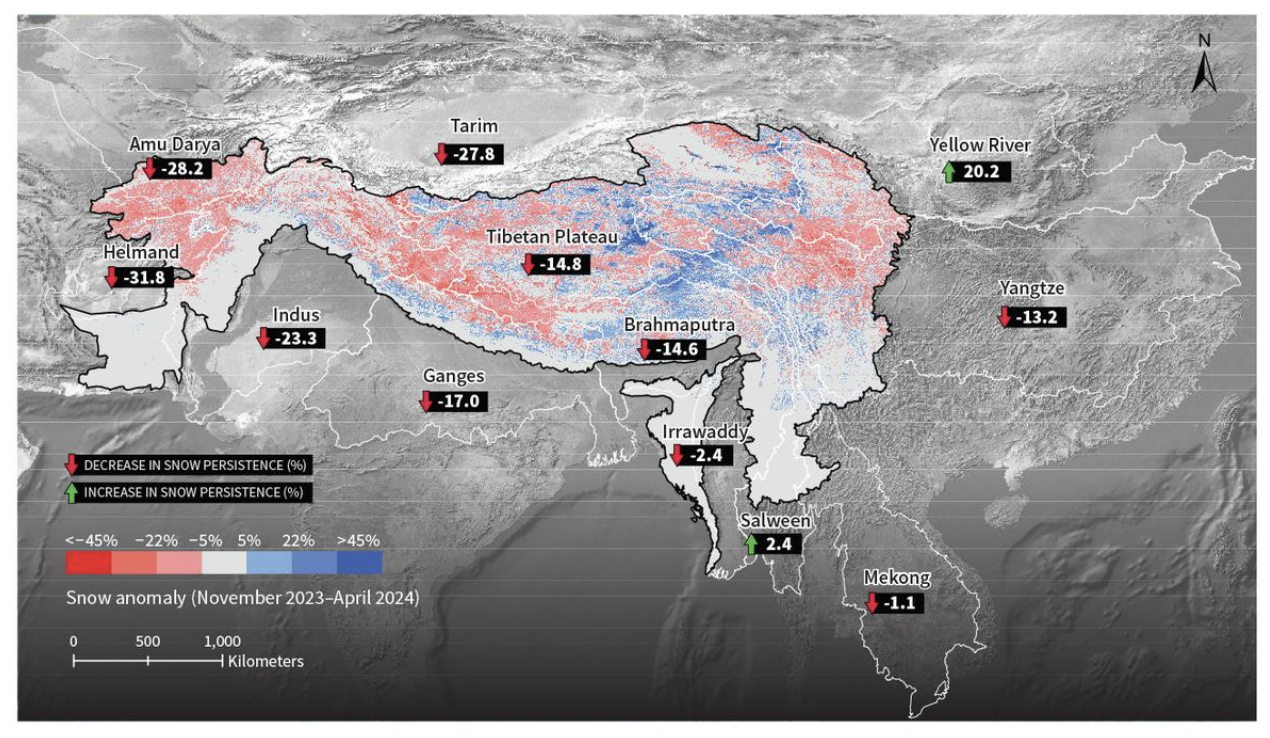
The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) has released its 2024 Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) snow update, highlighting significant declines in snow persistence across major river basins in the region.
Challenges highlighted by the update:
- This decline threatens the water supply for millions of people.
- The Ganga river basin, India's largest, recorded its lowest snow persistence on record in 2024.
- Similar trends were observed in the Brahmaputra and Indus basins.
- The situation underscores the accelerating climate crisis, which is outpacing scientists' projections and posing substantial challenges to one of the world's most populated regions.
Importance of Snow Persistence:
- Snow persistence refers to the fraction of time snow remains on the ground, which is crucial for water supply as it melts and feeds into streams and rivers.
- In the HKH region, snowmelt is a primary water source, contributing 23% of the annual runoff to the 12 major river basins.
- The HKH mountains, spanning approximately 3,500 km across eight countries (Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, Myanmar, and Pakistan), are often called the “water towers of Asia” because they source ten significant river systems, including the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus.
- These basins provide water to nearly a quarter of the world's population and serve as a vital freshwater source for 240 million people in the HKH region.
Findings from the 2024 Report
River Basin Analysis:
- Ganga Basin: The Ganga River basin saw its lowest snow persistence in 22 years, 17% below the historical average.
- The previous record low was in 2018, at 15.2% below normal.
- Brahmaputra Basin: Snow persistence was 14.6% below normal in 2024, with a previous low of 15.5% below normal in 2021.
- Indus Basin: Snow persistence fell 23.3% below normal, though some lower altitude areas experienced excesses.
International Comparisons Outside India:
- Amu Darya river basin in Central Asia recorded its lowest snow persistence in 2024 at 28.2% below normal.
- The Helmand River basin, crucial for Iran and Afghanistan, was nearly 32% below normal, surpassing the previous record set in 2018.
- The Mekong River’s origin area saw slightly below normal snow persistence.
Causes and Implications:
- Weak Western Disturbances led to low snow persistence in 2024 according to the experts from the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD).
- Western Disturbances originating over the Mediterranean, Caspian, and Black Seas, bring winter rain and snow to the HKH region.
- Persistently high sea-surface temperatures disrupted these systems, delaying their arrival and reducing winter precipitation and snowfall.
- Climate Change Factors: The pattern of high temperatures and altered weather systems, exacerbated by global warming, explains the record low snow persistence in 2024 and similar historical records.
- The experts emphasized that the 1.5 degrees Celsius limit set by the Paris Agreement is insufficient to protect the HKH's snow, ice, people, and ecosystems due to the higher real temperature increases in the region.
Regional Variations:
- Interestingly, the snow persistence in China's Yellow River basin exceeded the normal value by 20.2% in 2024.
- This was attributed to the East Asian winter monsoon, which brings cold, dry air from Siberia and Mongolia that interacts with moist air from the Pacific Ocean, resulting in snowfall over higher altitudes.
Importance of snow melts for water supply:
- Snowmelt is crucial for the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus basins, contributing significantly to their water supply.
- Snowmelt accounts for 10.3% of the Ganga's water, compared to 3.1% from glaciers.
- In the Brahmaputra and Indus basins, snowmelt contributes 13.2% and 40%, respectively, compared to lower glacier melt contributions.
Future Strategies:
- The decline in snow persistence in 2024 may impact water availability, particularly in the Indus basin, if early-season rainfall is insufficient.
- Long-term solutions include reforestation with native tree species to retain more snow, improving weather forecasting, and developing early warning systems.
- Enhancing water infrastructure and formulating policies to protect snowfall areas are also crucial.
Call to Action:
- Need to reduce emissions to mitigate increasing sea-surface and ground temperatures, which lower snow persistence.
- Stronger political will to cut fossil fuel consumption and production, especially among G-20 countries, which account for 81% of global emissions.
- Comprehensive solutions for the sustainability of snow require community involvement in decision-making and regional cooperation.
Conclusion:
The 2024 HKH snow update serves as a stark reminder of the urgent need for action to address climate change and its profound impacts on water resources and public health in the region.
|
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
|



