News Excerpt:
Following close on the heels of China's third and latest aircraft carrier Fujian completing its maiden test voyage, the Defence Minister of India stated that India would soon commence building its third aircraft carrier, adding that New Delhi has plans to make "five or six more".
Background:
- While the debate around carriers versus submarines continues, there is a renewed global as well as regional interest with several countries now going for carriers of varying sizes.
- Despite the considerable costs associated with acquisition and operation, it often presents a more cost-effective and flexible option compared to deploying and maintaining land-based air assets in foreign territories.
- The U.S. is fielding new super carriers, and the U.K. has inducted new carriers while France and Russia have announced plans to build new ones.
- Japan has begun converting its helicopter carriers to operate F-35 fighter jets.
- Last month, China announced that it is building its fourth aircraft carrier, likely a nuclear-powered carrier.
What is an Aircraft Carrier?
- An aircraft carrier is a large naval ship designed to carry military aircraft and features a long, flat deck for aircraft takeoffs and landings.
- These vessels function as floating air bases, equipped with a full-length flight deck for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft.
- They serve as command and control centres for a naval fleet during both wartime and peacetime operations.
India:
- At present, the Indian Navy operates two 45,000-tonne aircraft carriers, the INS Vikramaditya and the INS Vikrant. Both are conventionally powered and use ski-jump ramps to assist aircraft takeoff.
- The INS Vikrant, India's first indigenous carrier built by Cochin Shipyard Ltd, was commissioned in September 2022.
- The INS Vikramaditya, acquired from Russia, was deployed in 2014.
- India has tentatively dubbed its third aircraft carrier IAC-2 or INS Vishal, which will have a displacement of 65,000 tons.
- India needs these carriers due to the fragile maritime security situation across the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) and India’s stature as the largest resident naval power necessitates a strong and robust Navy.
China:
- At present, the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) operates two conventionally-powered, ski-jump ramp aircraft carriers, the 60,000 tonne-class Liaoning and Shandong.
- Unlike its predecessors, the 80,000 tonne-class Fujian (third Aircraft carrier) will launch its aircraft using three electromagnetic catapults.
- These catapults are powered by an electromagnetic system similar to that of the US Navy's Gerald R Ford-class carrier and are more advanced than the ski-jump mechanism used by Indian and other Chinese carriers.
- From commissioning its first carrier, Liaoning, in 2012, launching its second carrier Shadong in 2017, its third carrier Fujian in 2022 and the fourth to be unveiled soon, China’s pace is absolutely unprecedented in this regard.
- China’s carrier fleet is poised to become the second-largest in the world, eclipsed only by the United States’ staggering eleven active carriers.
Japan
- In April, Japan's Maritime Self-Defense Force (MSDF) unveiled its upgraded helicopter carrier Kaga, after completing the first stage of modifications to turn the warship into an aircraft carrier.
- The Kaga is one of the two Izumo-class helicopter carriers operated by Japan's MSDF.
- Izumo, the second ship of the class, is also undergoing similar modifications.
South Korea
- The military has urged accelerating plans for developing a next-generation carrier, marking the initial phase of acquiring core design and construction technologies.
- Initially targeting a 40,000-tonne carrier capable of operating F-35B jets, the project is aimed for completion by 2024.
Significance of Aircraft Carriers:
An aircraft carrier is fundamental to command, control, and coordinate operations from the sea and to project combat power ashore, over the seas, or in the air. These are extremely significant in the following aspects:
- Offensive and Defensive Capabilities: Aircraft carriers facilitate offensive operations, including bombing raids, conducted from the sea. In addition to it, they defend against air threats, such as hostile aircraft or missiles, and possess advanced defensive technologies.
- Power Projection: Aircraft carriers enable countries to project military power across vast distances, deterring hostile actions.
- Increased Air Support: They provide significant air support by launching and recovering aircraft at sea, aiding ground forces globally.
- Versatility: Carrying various aircraft, they execute diverse missions worldwide and swiftly reposition during operations.
- Intelligence Gathering: Aircraft carriers deploy reconnaissance aircraft to gather enemy intelligence and conduct electronic surveillance.
- Humanitarian Aid: They serve in humanitarian missions, offering aid during crises, as demonstrated by the USS Abraham Lincoln's response to the 2004 Southeast Asia earthquake and tsunami.
|
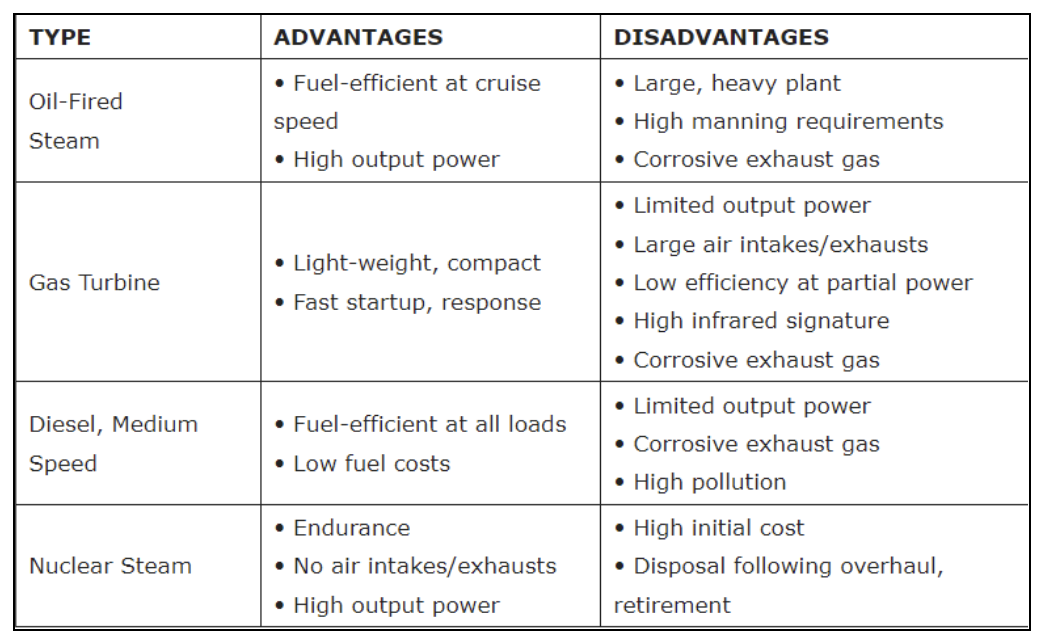
Types of propulsion systems
(1) Oil-fired steam (2) Diesel fired (3) Gas turbine
The following table lists the advantages and disadvantages of these propulsion systems:
|