News Excerpt:
Recently, Scientists Discovered How to Control the Casimir Effect—and Supercharge Tiny Machines.
|
What is Casimir Effect:
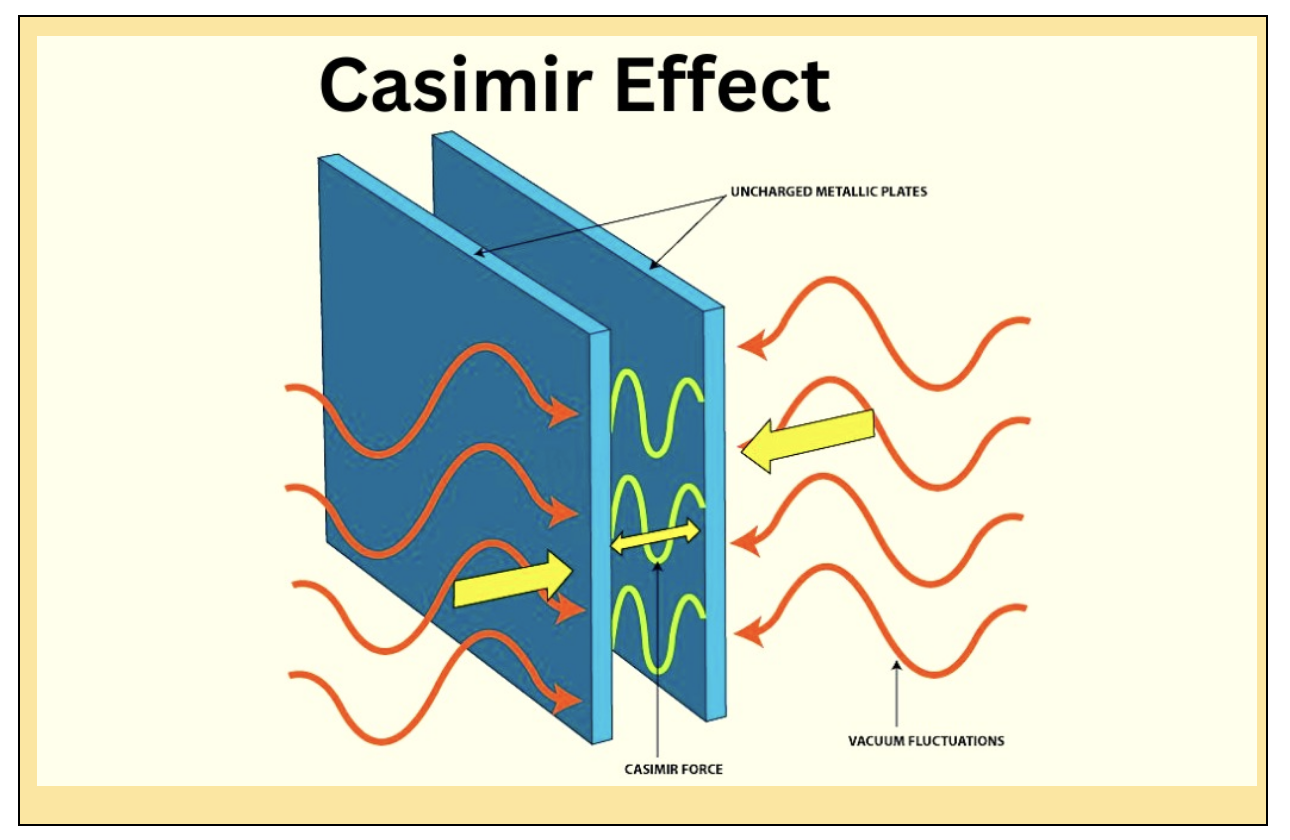
- The Casimir effect is a quantum phenomenon in which two materials, when placed close together, can be attracted or repelled by quantum fluctuations.
- In 1948, Dutch physicist Hendrik Casimir along with one of the fathers of quantum physics, Neils Bohr—developed an ingenious experiment to witness the invisible wonders of quantum mechanics.
- Casimir placed two electrically neutral plates within one micrometer of each other in a vacuum.
- The plates were pulled together via the invisible quantum fluctuations that permeate spacetime.
- The Casimir effect is a small attractive force that acts between two close parallel uncharged conducting plates. It is caused by quantum vacuum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field.
|
About the study:
- A new study from researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences reports that they’ve successfully manipulated the Casimir effect by reversing the transition from attractive to repulsive.
- They used a ferrofluid—a fluid that can be manipulated using magnetic fields—as an intermediate medium.
- The researchers used magnetic fields to create a reversible transition from Casimir attraction to repulsion.
- The ability to control the Casimir effect in this way could be a big breakthrough for engineering nanotechnology, which is often designed with the Casimir effect in mind.
Post-Casimir development:
- After 50 years the Yale physicist Steve Lamoreaux, measured this incredibly small effect.
- However, with the rise of nanotechnology during that same period, understanding the Casimir effect and its impact on these incredibly small machines became vitally important.
|
Nanotechnology:
- Nanotechnology involves the understanding and control of matter at the nanometer-scale.
- Nano-scale deals with dimensions between approximately 1 and 100 nanometers.
- On the nanometer-scale, materials may exhibit unusual properties.
- For example: Change in the size of a particle can change the color of the particle because the arrangement of atoms reflects light differently. Gold can appear dark red or purple, while silver can appear yellowish or amber-colored.
- Nanotechnology can increase the surface area of a material. This allows more atoms to interact with other materials.
- It can be stronger, more durable, and more conductive than their larger-scale (called bulk) counterparts.
|



