News Excerpt:
Small farm holders from 10 villages in Mokokchung district of Nagaland are setting an example in replacing plastics with compostable bioplastic bags made from Cassava starch.
|
Amendments to India’s Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2024, defines biodegradable plastics as those plastics which are capable of degradation by biological processes in specific environments such as soil and landfill, and in addition they should not leave any microplastics behind. |
Significance of the innovation:
- Efforts of the Government to ban single use plastic has made limited impact mainly due to lack of alternative lightweight materials that can replace the widely used plastics.
- In order to address this challenge North East Centre for Technology Application and Reach (NECTAR) has supported an initiative to manufacture Compostable Bioplastic Bag from Cassava Starch (Manihot esculenta).
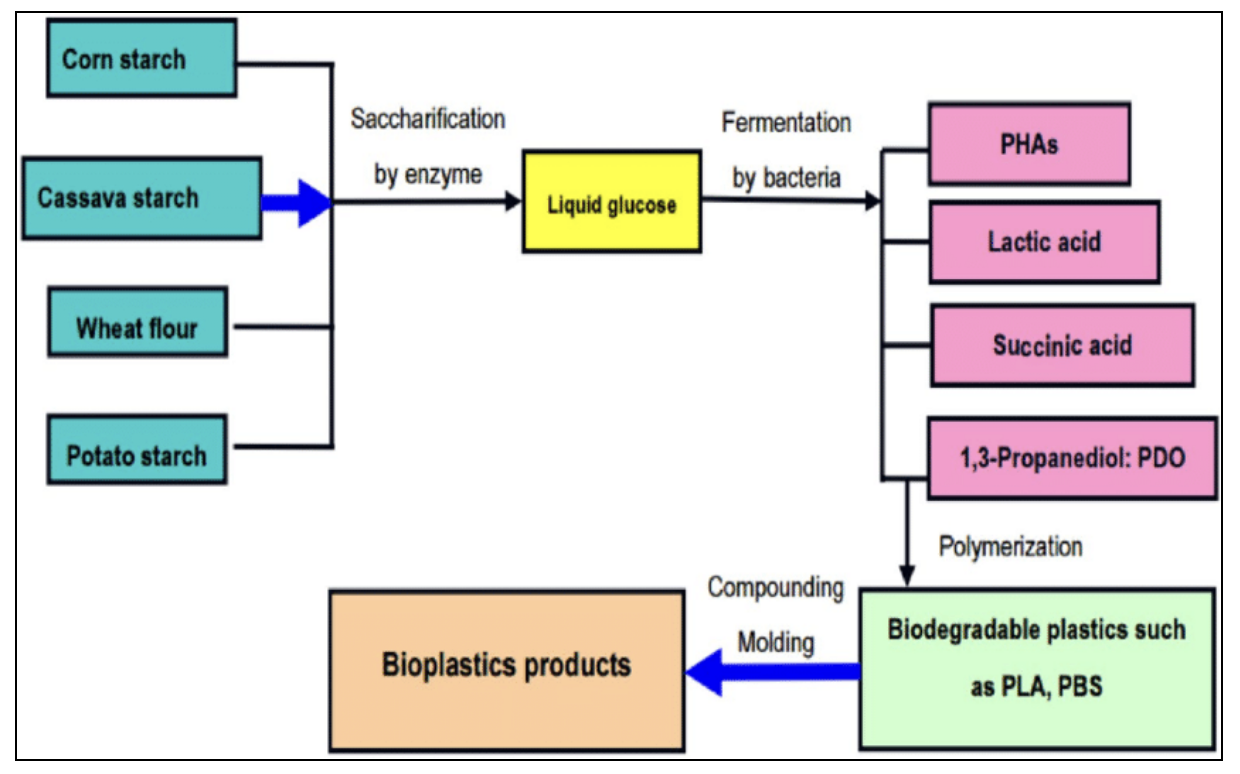
- The steps involved in converting plant based starch into bioplastic is shown in the following image.
Community based initiative:
- Ecostarch, a Nagaland based MSME, has set up a facility to manufacture bioplastic bags from Cassava plant in Mokokchung, Nagaland and is mobilizing farmers within 30-40 km range of the production facility to take up Cassava farming.
- The farmers have already started with the plantation of materials and in about a year it will be ready for harvest.
- The current production capacity of the unit is about 3 tons per month and the market survey has revealed demand for more.
Boost to local economy :
- Through this model, ‘cassava village’ is being promoted to boost local economy and provide employment opportunity to local youth.
- Formation of farmer groups are being facilitated to provide them with alternative livelihood opportunities through cassava farming.
- Farmers are also being trained on cassava cultivation and equipped with useful farming inputs.
- Women SHGs (Self Help Groups) operating in all the targeted villages are also being strengthened and encouraged to take up cassava cultivation as their IGA (Income Generation Activities).
Way Ahead:
- Ecostarch aims to set up a biodegradable films/bags manufacturing unit suitable for food packaging and carry bags made of cassava starch sourced locally from farmers.
- This could employ more local youth in cleaning of raw materials, sorting and packaging of products for shipping.
- The effort has started an environment friendly plastic economy in the region creating a greener economy.
- It is expected to act as a potential employment generation activity. It is on the way to transform each village into an enterprising hub, create a greener cyclic economy and bring about much needed economic freedom among the farmers in the rural areas.
|
Cassava Starch (Manihot esculenta)
|