News Excerpt:
Scientists have warned that the 'crossbreeding' between different viruses may lead to the emergence of a completely new, altered virus with potentially more threatening characteristics.
More about the news:
- According to researchers, most of the viruses are still unknown to humans as scientific studies have focused more on viruses that cause diseases in humans, domestic animals, and crops.
- The nidoviruses discovered in fish frequently exchange genetic material between different virus species, even across family boundaries.
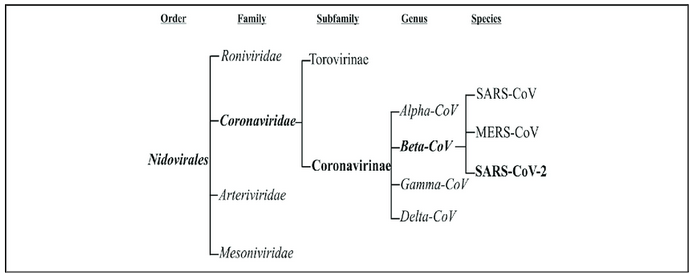
What are Nidoviruses?
-
Nidoviruses are a diverse group of enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA (Ribonucleic acid) viruses belonging to the order Nidovirales.
-
This order includes several virus families such as Coronaviridae (coronaviruses), Arteriviridae (arteriviruses), and Roniviridae (roniviruses), among others. They have unique features distinguishing them from other RNA viruses.
Concerns regarding the findings:
- Such viruses may even trigger another COVID-19-like pandemic.
- A natural evolution of viruses occurs as different virus species create new pathogens inside vertebrates.
- Evolution among viruses is more glaring and radical when two viruses from totally different families interact.
- Such evolution may lead the virus to cause fatal and dangerous diseases to the host animal.
- Genetic exchange as found in the fish viruses, will probably also occur in mammalian viruses according to the study.
- Such natural crossbreeding (exchange of genetic material) processes among viruses may easily take place in bats that are known to carry a large number of viruses inside their bodies.
- After gene exchange between nidoviruses, the spike protein with which the viruses dock onto their host cells often changes.
- Viral "game changers" can suddenly appear at any time, becoming a massive threat and triggering a pandemic. The starting point can be a single double-infected host animal.
Significance of the study:
- The new high-performance computer process could help to prevent the spread of new viruses.
- It enables a systematic search for virus variants that are potentially dangerous for humans.
- This can be used to systematically examine cancer patients or immunocompromised people for viruses.
- The use of the new AI-assisted method led to the discovery of 40 previously unknown nidoviruses in various vertebrates from fish to rodents. It also included 13 new coronaviruses.
Conclusion:
The discovery of new nidoviruses and the role of viral crossbreeding in creating potentially dangerous pathogens highlight the urgent need for comprehensive surveillance and advanced analytical methods. Understanding these processes is crucial for preventing future pandemics, emphasizing the importance of continuous research and monitoring to safeguard global public health.


