GS Paper I
News Excerpt:
India has slipped two places on the World Economic Forum's (WEF) Global Gender Gap index to 129th place, while Iceland retained its top position in the rankings.
Key findings from the Global Gender Gap Index:
Global:
- The world has closed 68.5% of the gender gap, but at the current pace, it will take another 134 years to achieve full gender parity.
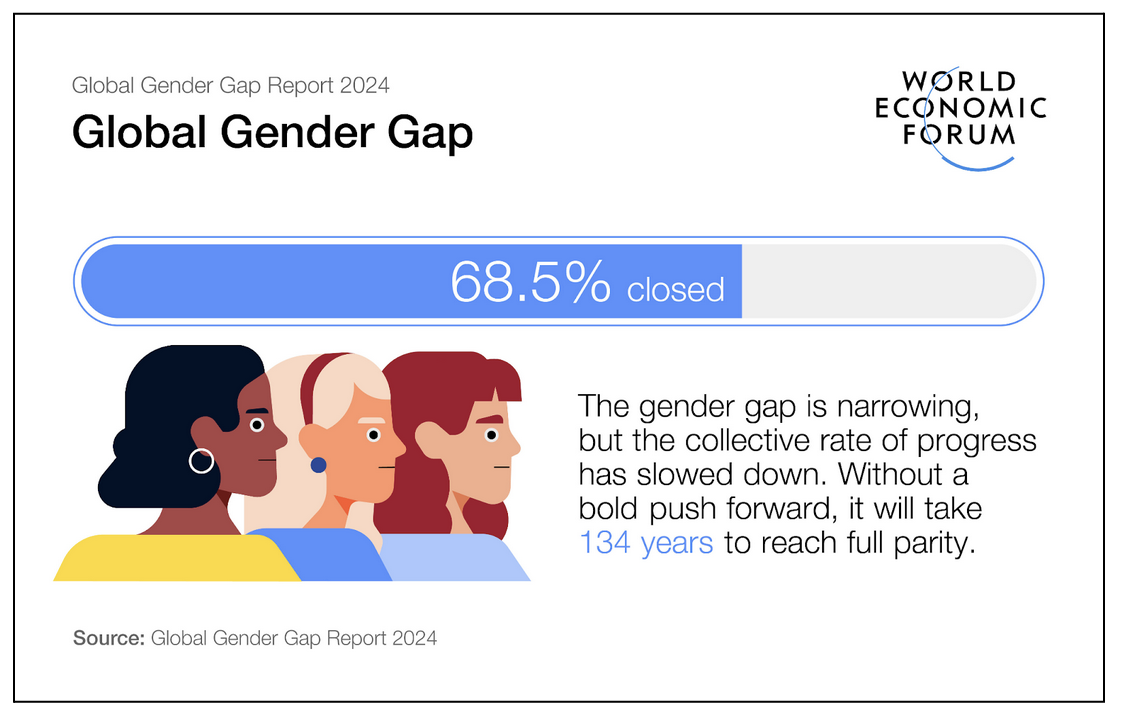
- Iceland was ranked first in the Global Gender Gap Index, followed by Finland, Norway, New Zealand, and Sweden in the top five.
- Sudan was ranked last on the index of 146 countries, while Pakistan slipped three places to 145th.
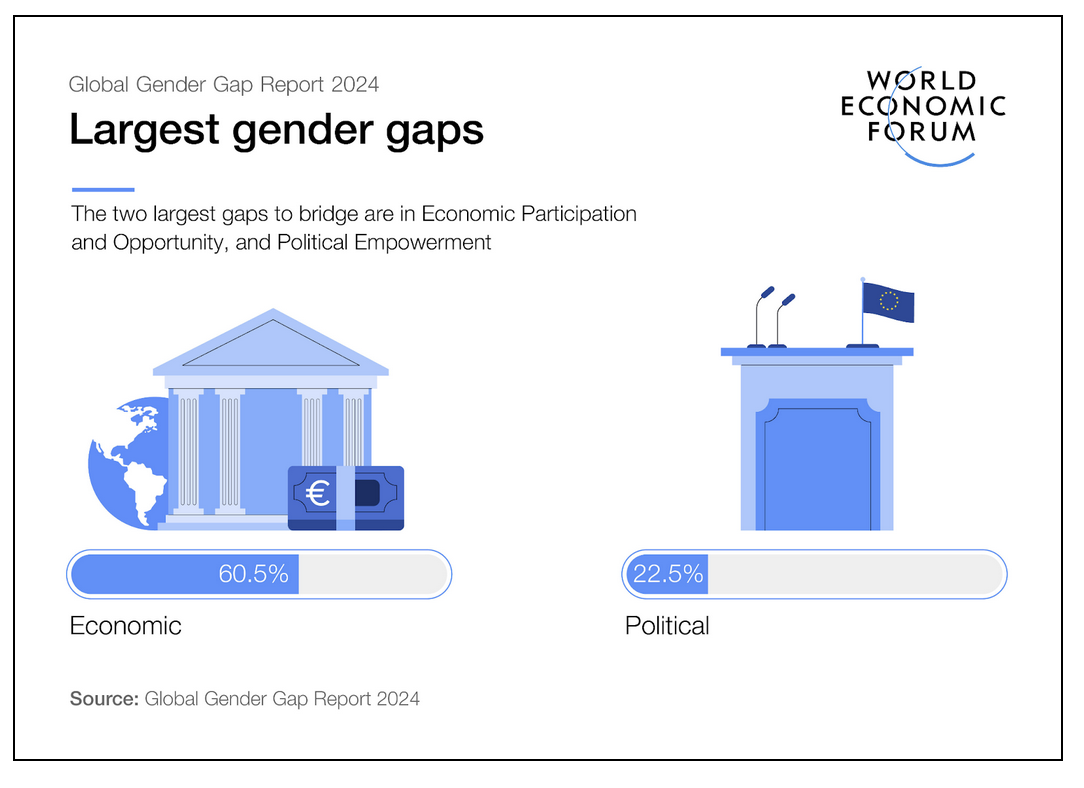
Largest Gender Gap:
- Overall, the most significant shift occurs in Political Empowerment, where parity has jumped a total of 8.3 percentage points to 22.8% over the past 18 editions. In Economic Participation and Opportunity and Educational Attainment, parity has gained 4.8 and 4.2 percentage points respectively.
- In Political Empowerment, Europe shows a consistent upward trajectory, achieving the highest level of political parity among all regions in 2024, with 36%. Latin America and the Caribbean follow closely behind, with 34%.
- The Economic Participation and Opportunity score for the region is 71.7%, showing progress since 2023 but revealing significant disparities between countries in labour-force participation rates and workforce representation.
- Despite North America leading in the Economic Participation and Opportunity subindex, its economic parity score has declined slightly to 76.3%, reflecting disparities in earned income and women’s representation in senior leadership positions
India-Specific:
- India was ranked 127th out of 146 countries in the Index.
- Within South Asia, India was ranked fifth after Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Bhutan, while Pakistan was ranked last.
- India figured among the economies with the lowest levels of economic parity, alongside Bangladesh, Sudan, Iran, Pakistan, and Morocco, with less than 30% gender parity in estimated earned income.
- India showed the best gender parity in terms of enrollment in secondary education and scored well on the political empowerment of women, ranking 65th globally.
- India was ranked 10th in terms of parity in the number of years with female/male heads of state for the last 50 years.
- India has closed 64.1% of its gender gap in 2024, a decline of two places from 127th last year mainly due to small declines in 'Educational Attainment' and 'Political Empowerment' parameters.
- India's economic parity score has trended upward for the past four years.
- India scored within the top 10 on the head-of-state indicator but has relatively low scores for women's representation at the federal level, in Ministerial positions (6.9%), and in Parliament (17.2%).
Women- Specific:
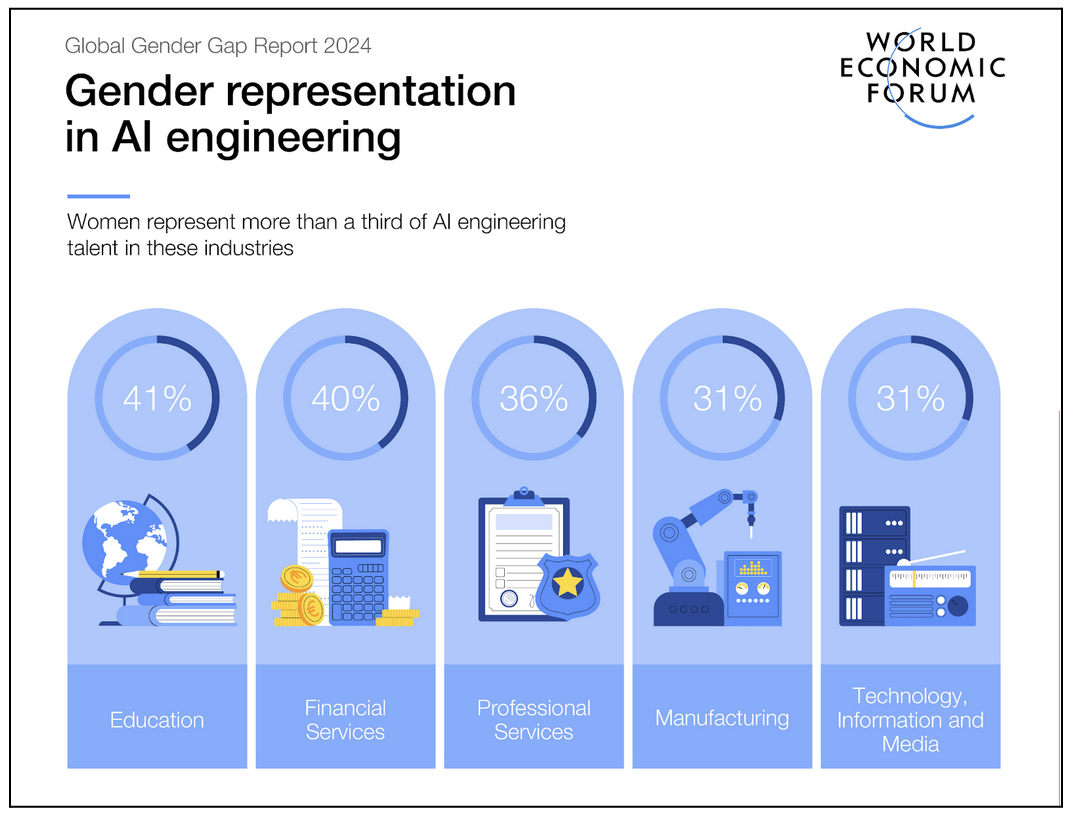
- Gender gaps in AI talent: Recent developments show more promising trends in AI talent specifically. As technology plays a crucial role in business transformation, recent LinkedIn data indicates a significant increase in the concentration of female talent in AI engineering, more than doubling since 2016.
- While women continue to have a smaller presence in the industry compared to men, sectors such as Technology, Information, and Media have witnessed notable growth in female AI talent.
- At the industry level, gender parity in AI representation has gradually improved in sectors including Education, Professional Services, Manufacturing, and Technology, Information, and Media
- Women's representation in senior leadership has fared slightly better than their overall workforce representation, with a less pronounced drop in recent years.
- LinkedIn data from the past eight years shows that women increased their representation in leadership roles, from a 30.4% share in 2016 to a 32% share in 2023.
- Gender gaps in AI talent: Recent developments show more promising trends in AI talent specifically.
- As technology plays a crucial role in business transformation, recent LinkedIn data indicates a significant increase in the concentration of female talent in AI engineering, more than doubling since 2016.
- At the industry level, gender parity in AI representation has gradually improved in sectors including Education, Professional Services, Manufacturing, and Technology, Information, and Media.
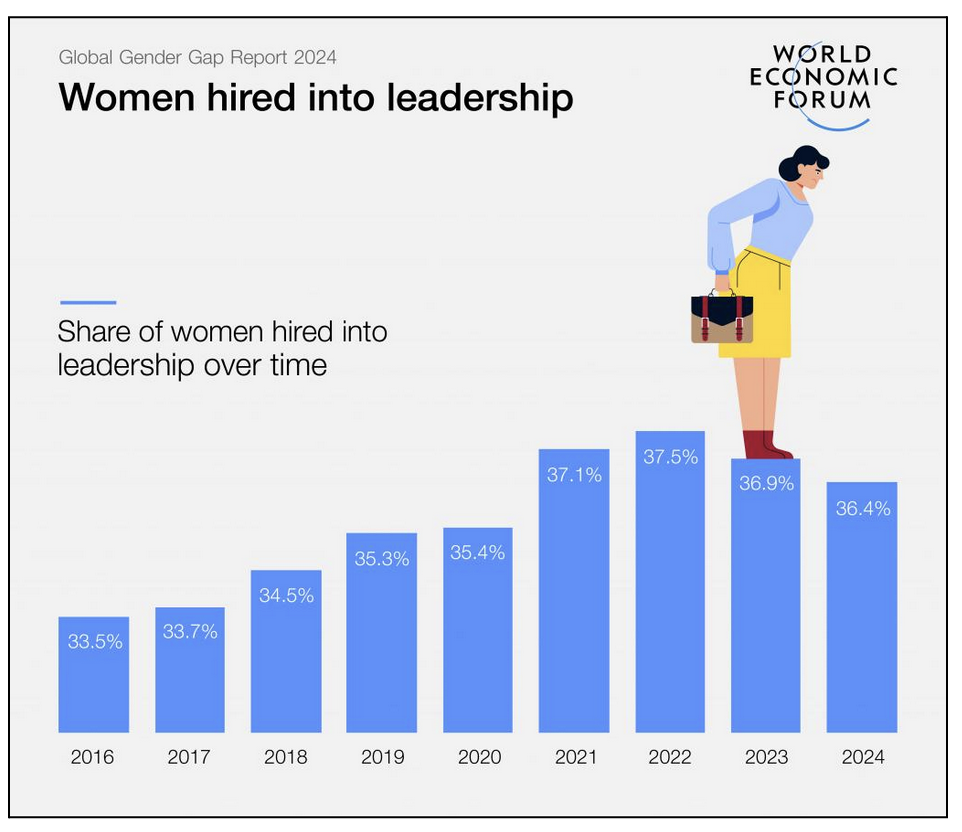
- Women's representation in senior leadership has seen modest improvements since 2016, with more women in senior leadership across every industry in 2024 than in 2016.
- This relationship is especially pronounced in industries with under 50% female representation in the workforce, and it is not the result of fewer women applying to such roles.
- The industries where the effect of labor market tightness on hiring rates of women into leadership roles is most pronounced include Oil, Gas and Mining, and Construction.
|
Global Gender Gap Index
|
Conclusion:
- Despite some bright spots, the slow and incremental gains highlighted in this year's Global Gender Gap Report underscore the urgent need for a renewed global commitment to achieving gender parity, particularly in economic and political spheres.
- According to WEF, the world cannot wait until 2158 for gender parity, the time for decisive action is now.



