News Excerpt:
On May 5, the CEO of a marketing research firm received an anonymous email claiming access to Google’s Search algorithm API documents. This leak exposed significant insights into Google's ranking factors.
What are search engines?
- Search engines are programs that enable users to search and access information from the extensive content available on the internet.
- They utilize algorithms to index and rank web pages according to their relevance to a user's query, presenting a list of results for users to browse.
- Popular search engines include Google, Bing, and Yahoo.
How does a search engine work?
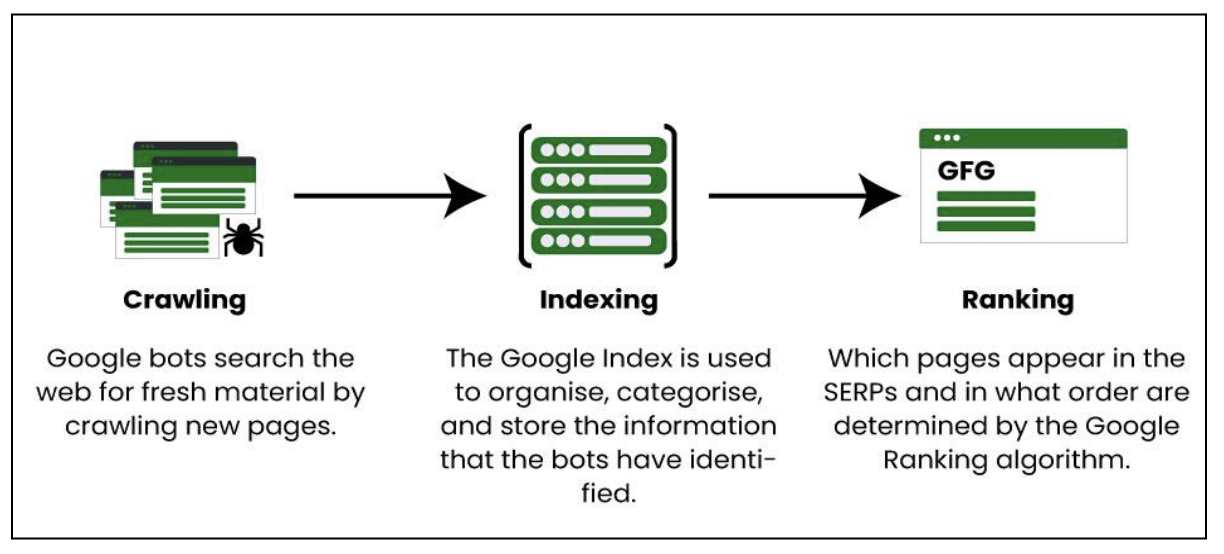
Search engines operate through three primary processes: Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking.
- Crawling: This involves search engines using programs called crawlers to discover publicly available information on the internet. Crawlers scan the web to create a list of websites, visiting each to understand its structure, content type, and updates by reading the HTML code. Crawling is crucial because if search engines can't find your content, it won’t appear in search results, impacting your ranking and traffic.
- Indexing: After crawling, the gathered information is organized, sorted, and stored for later processing by the ranking algorithm. Search engines don’t store all data but keep essential details like the page title, description, content type, associated keywords, and links. Indexing is vital because only indexed pages can appear in search results, increasing your chances of being found for related queries.
- Ranking: This determines the position of your website in search engine results. Ranking involves several steps to evaluate various factors about the indexed pages to decide their order of appearance in response to a search query, ultimately influencing your website's visibility and traffic.
Steps involved when we hit the search for a query on the search engine:
Step 1: Analyze user query: Break down the query into meaningful keywords to understand user intent, including interpreting synonyms and correcting spelling mistakes.
Step 2: Finding matching pages: Search the index for the best matches; for instance, a search for "dark wallpaper" yields image results.
Step 3: Present results: Display results, typically ten organic links, alongside ads and direct answers.
Significant impact of the reveal:
- While the documents did not reveal the exact factors influencing Google's Search ranking, they exposed a list of tracked factors.
- This transparency is significant as Google has historically kept its algorithm as secretive as a black box.
- Company executives have often been silent about the ranking process, deceiving marketing professionals and content creators whose work relies on optimizing content for Google Search.
Conclusion:
This leak is reminiscent of AOL’s 2006 incident, where 20 million keyword searches from 650,000 users were accidentally released. While Google’s leak is not as severe, it serves as a reminder for journalists and SEO professionals to question the company’s claims.
Google admitted the data's authenticity but cautioned against making assumptions based on potentially outdated or incomplete information. However, this leak challenges the credibility of Google’s past statements.


