News Excerpt:
SpaceX's Starship rocket achieved a significant milestone with its first fully successful test flight, its booster and spacecraft executed a gentle splashdown after an hour-long sub-orbital journey.
More about the news:
This marked SpaceX's fourth attempt to launch the colossal Starship, bringing it one step closer to revolutionizing space travel and exploration.
Starship:
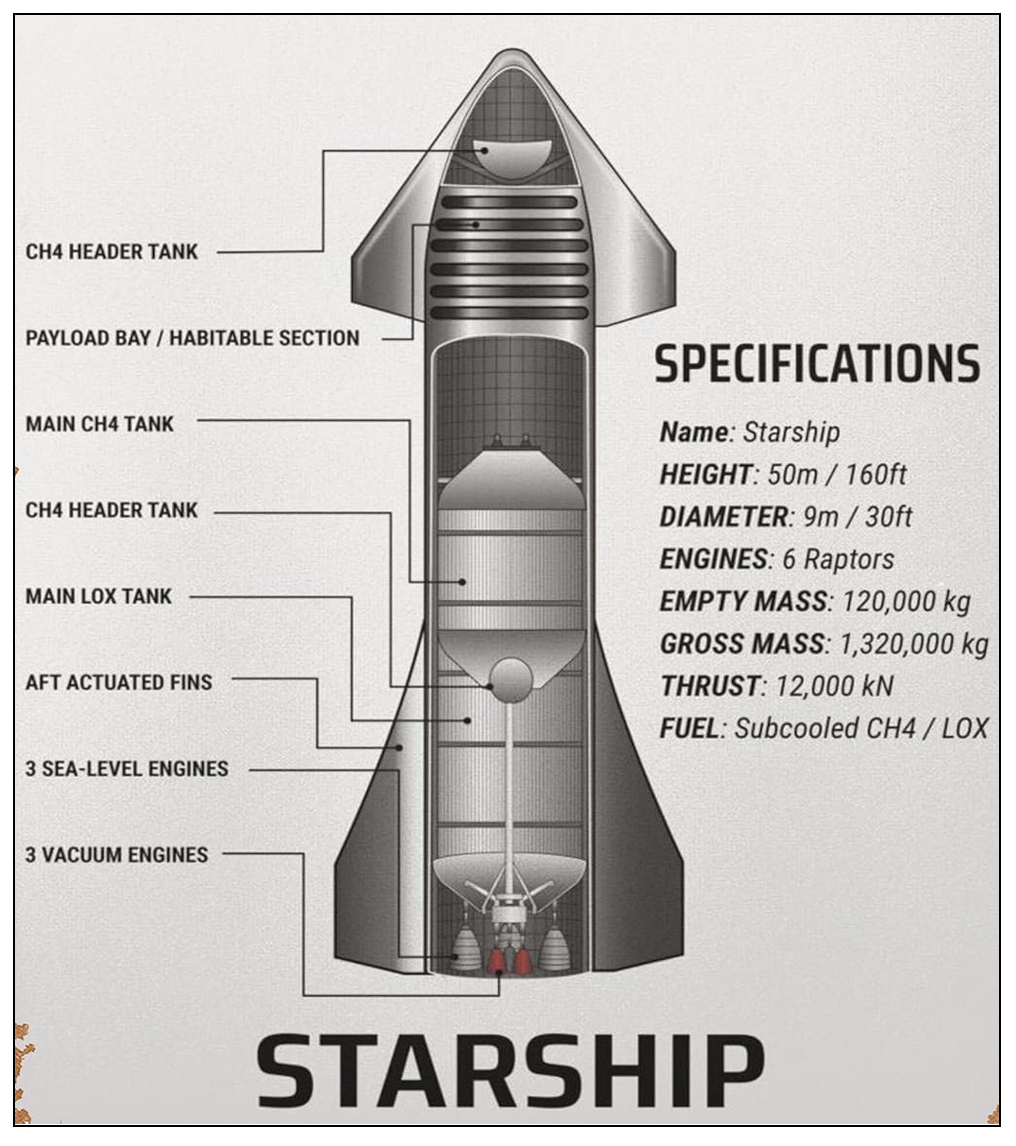
- Starship is a two-stage heavy lift-off vehicle designed to transport crew and cargo to Earth orbit, the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
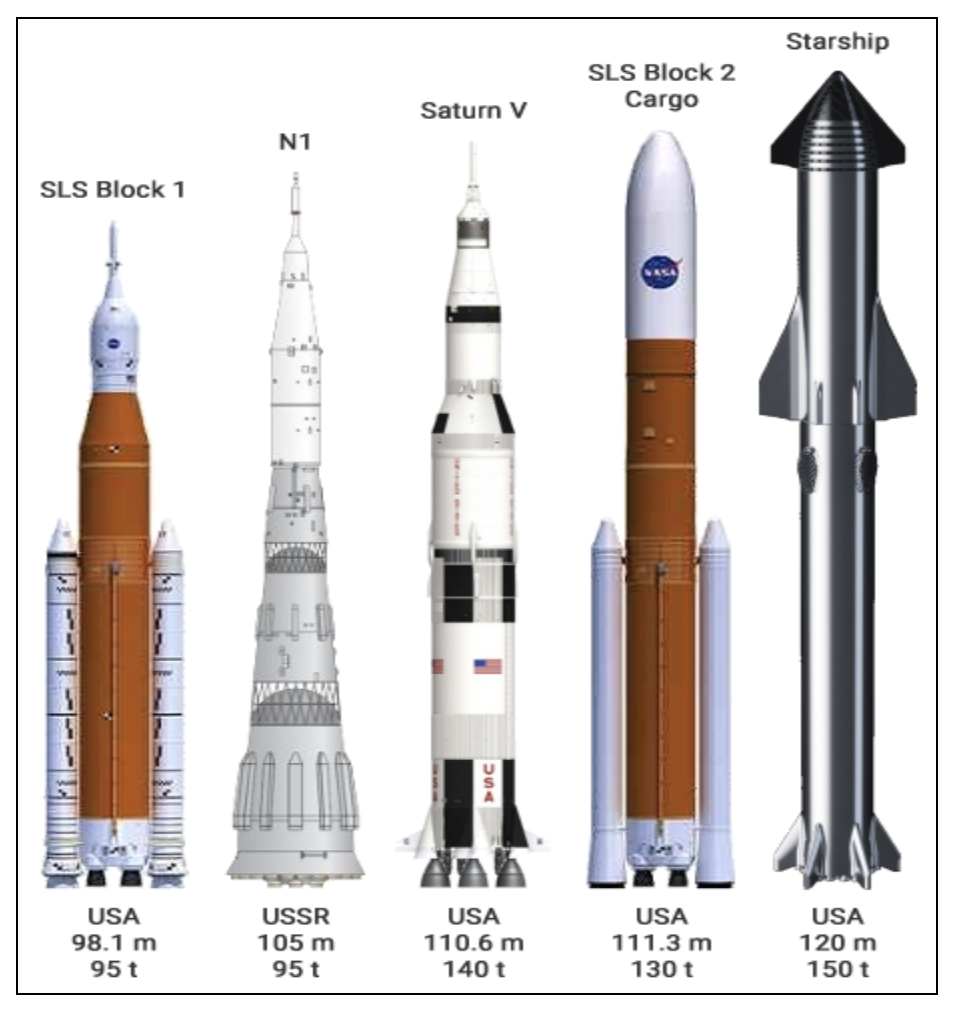
- It is the largest rocket ever flown, its height is 120m surpassing the Saturn V which was 111m (carried Neil Armstrong to the Moon).
- The rocket's lower stage, known as Super Heavy, comprises 33 Raptor engines generating 74 meganewtons of thrust, nearly double that of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) and the Saturn V.
These engines use a mixture of liquid oxygen and liquid methane, enhancing efficiency and reusability.
Significance of the development:
Reducing the Cost of Space Travel facilitated by:
- High Payload Capacity: Starship is expected to carry up to 150 tonnes of payload to low-Earth orbit and at least 100 tonnes to the Moon and Mars which exceeds all previous missions, enabling more extensive scientific and commercial activities in space.
- In-Orbit Refueling: SpaceX is developing the capability to refuel Starship in Earth orbit using other Starships.
- This innovation allows for increased payload capacity and the use of more advanced scientific instruments, effectively operating like an airplane that can be quickly refueled and redeployed.
- Complete Reusability: Unlike other launch systems where hardware is often discarded, Starship’s principal components are designed to be fully reusable.
- Both the Super Heavy booster and the Starship spacecraft can re-enter Earth’s atmosphere and land back at the launch site, significantly reducing costs associated with building new rockets for each mission.
Facilitating Space Exploration
- This will enable scientists to launch larger and more sophisticated space telescopes, built from heavier but cheaper materials.
- Future missions to the Moon and Mars could carry substantial equipment, such as full-sized drilling rigs, to explore the planets' interiors and uncover valuable resources.
- Moreover, Starship’s ability to return to Earth means it can bring back large quantities of samples from the Moon and other planets, aiding scientists in unraveling the mysteries of our solar system and the origins of life.
- The rocket system is also integral to NASA's Artemis program
- It aims to return astronauts to the Moon by 2030 and to send humans to Mars by the end of the next decade.
Challenges
- SpaceX must still prove Starship’s safety, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Historical challenges, such as those faced by NASA’s Space Shuttle program, highlight the difficulty in making reusable spacecraft economical.
- Additionally, while Starship's development has been rapid compared to other launch vehicles, it has not been without setbacks.
- Balancing rapid innovation with safety and reliability remains a critical challenge for SpaceX.
- The accelerated pace of development at SpaceX has led to at least 600 previously unreported workplace injuries, raising concerns about the safety and well-being of employees.
Conclusion
SpaceX's Starship promises to redefine space travel by making it more affordable and accessible. With its high payload capacity, in-orbit refueling capabilities, and complete reusability, Starship is set to unlock new possibilities for scientific exploration and commercial ventures in space. However, ensuring the safety and reliability of the system while maintaining low costs will be essential to realize its potential fully.
|
Artemis
|
PRIVATE SPACE COMPANIES
|
|
Space travel and exploration
|