GS Paper III
News Excerpt:
India is planning to soon sign new and updated mineral pacts with about a dozen countries in Africa.
More about the news:
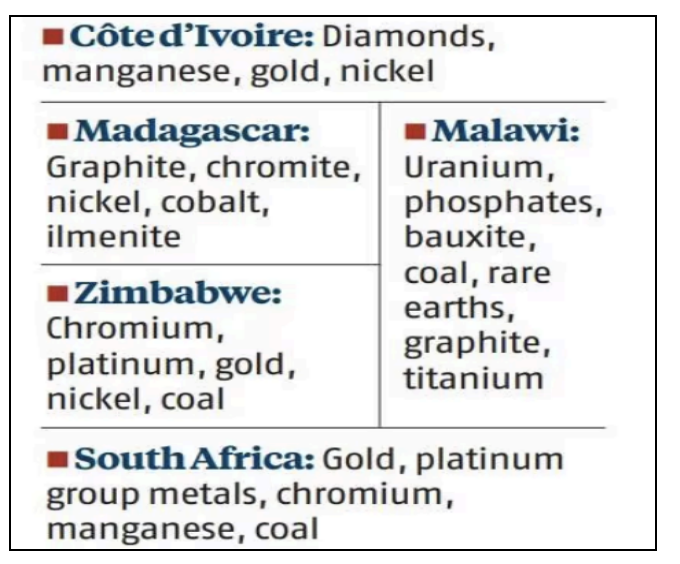
- The Ministry of Mines is in discussions with Côte d'Ivoire, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Morocco, Mozambique, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
- The aim of these mineral agreements will encompass not only meeting the demand for critical minerals but also addressing all of India’s mineral requirements.
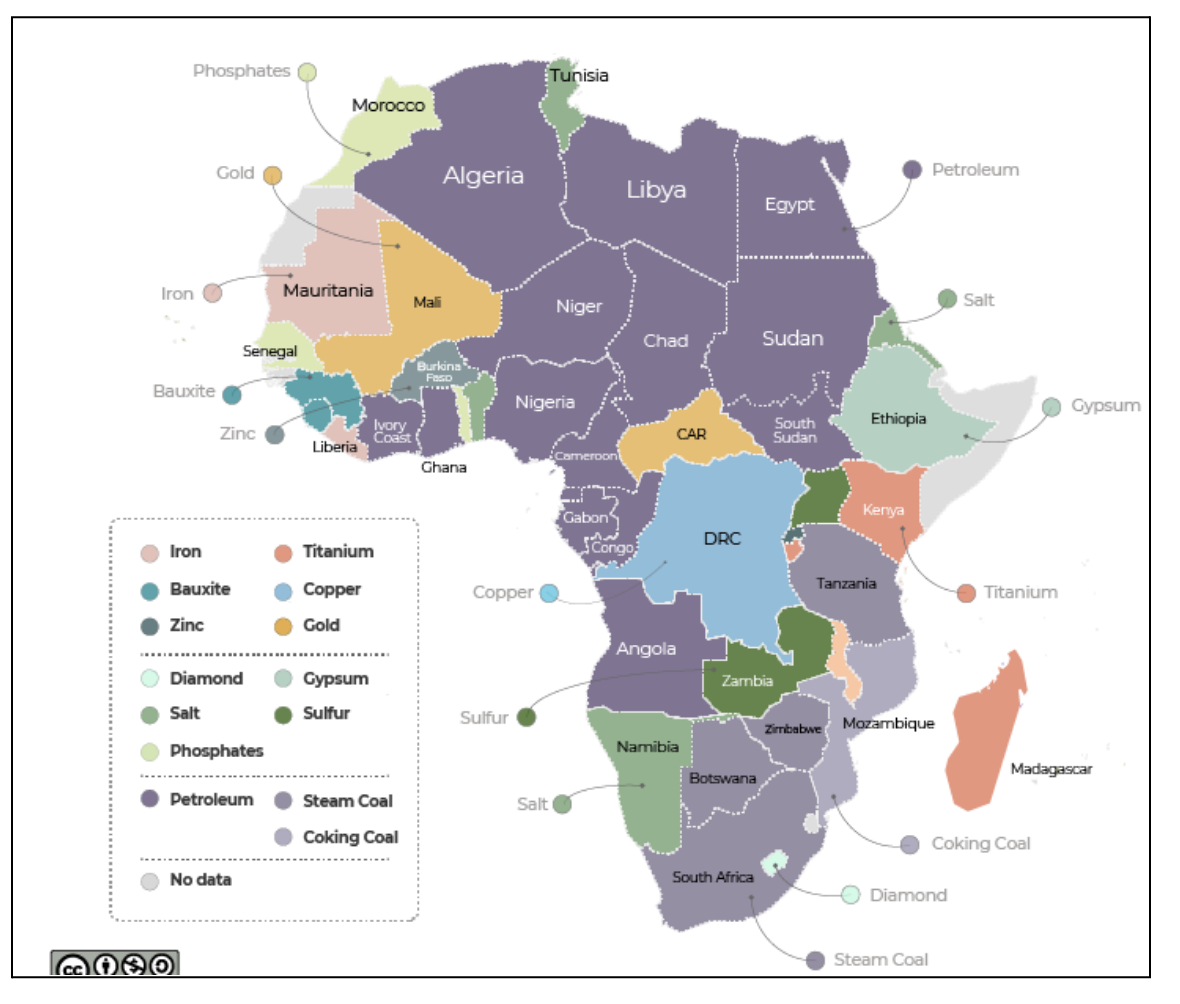
Abundance of Minerals in Africa: Cobalt, nickel, graphite, diamonds, platinum, and uranium are major minerals found in Africa, presenting lucrative opportunities for resource acquisition.
What is a critical mineral?
Critical minerals are natural resources that are deemed essential for a nation's economic and industrial development due to their significant role in various high-technology and strategic sectors.
The classification of minerals as "critical" is based on their scarcity, economic importance, and the potential risks associated with their supply chain disruptions or geopolitical conflicts.
Significance of critical minerals in an economy:
- Critical minerals are essential for India's economic growth and technological advancement due to their vital role in various industries such as electronics, defence, and renewable energy.
- Securing a stable supply of critical minerals ensures national security, reduces dependence on imports, and supports indigenous manufacturing capabilities.
- They are crucial for the production of advanced technologies like electric vehicles, batteries, and solar panels, driving innovation and sustainable development in the Indian economy.
India's Engagement with African Countries: India has Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs) with six African countries — Malawi, Mali, Morocco, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe — indicating a commitment to bilateral cooperation in the mining sector.
- Participation in multilateral initiatives like the International Solar Alliance and Global Biofuel Alliance strengthens India's ties with African nations.
Involvement of Public and Private Sectors:
- Alongside central agencies, private players, including Vedanta Group, Jindal Steel & Power, Samta Mines & Minerals, and Ashapura Group of Companies, are invited to participate in exploration, mining, and mineral trading in Africa.
- Leveraging the expertise of existing Indian mining firms in Africa is part of the strategy to expand operations in the continent.
Challenges Posed by China's Dominance:
- China's significant presence in Africa, facilitated by initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative, poses challenges to India's mineral procurement efforts.
- Chinese companies have secured access to key minerals like cobalt and lithium in African countries, potentially impacting India's access to these resources.
India's Response and Strategy:
- India is accelerating the pace of auctioning mines, particularly focusing on critical minerals to meet its mineral demand.
- The government released its first critical minerals list in 2023 and initiated the first round of critical minerals auctions in the same year.
- Currently, 38 critical mineral blocks are up for auction, demonstrating India's proactive approach to securing essential resources.
- A joint venture company namely Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL) has been incorporated to identify and acquire overseas mineral assets of a critical & strategic nature such as Lithium, Cobalt & others to ensure supply-side assurance.
Conclusion:
India's quest for minerals in Africa is a need of the hour but it poses challenges. China's dominant presence underscores the need for strategic planning and engagement at the government level. India's proactive approach, including collaboration with both public and private sectors, aims to address these challenges and ensure access to vital minerals for its industrial and economic development.
|
The Indian government has released a list of 30 critical minerals for India. These minerals are Antimony, Beryllium, Bismuth, Cobalt, Copper, Gallium, Germanium, Graphite, Hafnium, Indium, Lithium, Molybdenum, Niobium, Nickel, PGE, Phosphorous, Potash, REE, Rhenium, Silicon, Strontium, Tantalum, Tellurium, Tin, Titanium, Tungsten, Vanadium, Zirconium, Selenium and Cadmium. |


