News Excerpt:
Researchers at the Department of Biochemistry, Indian Institute of Science, have developed a novel method for producing recombinant proteins.
Currently used methods:
- Recombinant proteins, such as vaccine antigens, insulin and monoclonal antibodies, are mass-produced by growing modified bacterial, viral or mammalian cells in large bioreactors.
- The most widely used organism is the yeast Pichia pastoris (now called Komagataella phaffii).
Limitation of method used:
- Traditional mass production using yeast cell factories relies on methanol, which is flammable.
- It can also produce harmful byproducts like hydrogen peroxide which can induce oxidative stress in the yeast cells or damage the recombinant proteins.
Process of recombinant protein synthesis:
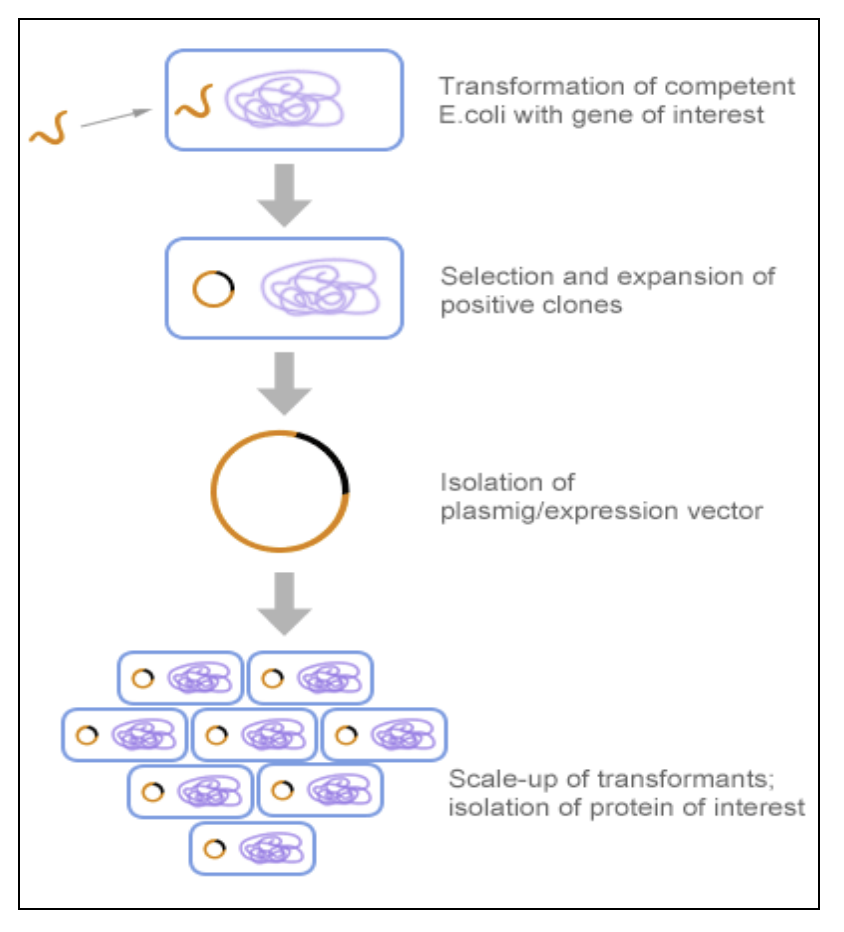
Significance of the research:
- After an extensive search, the team found that monosodium glutamate (MSG), a USFDA-approved food additive, can activate a different promoter in the yeast genome that codes for an enzyme called phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK).
- Activating PEPCK with MSG led to protein production similar to methanol activation of the AOX(Alcohol oxidase) promoter.
- This system can be used in biotech industries to mass-produce valuable proteins, including milk and egg proteins, baby food supplements, and nutraceuticals, as well as therapeutic molecules.
|
Recombinant protein:
|


