News Excerpt:
In September 2024, a once-in-a-lifetime nova explosion 3,000 light-years away from Earth is expected to light up our night sky.
What is a Nova Explosion?
- Nova explosion occurs when a star, as it interacts with a nearby star, undergoes a massive thermonuclear explosion.
- This event happens repeatedly over time in some star systems.
- This phenomenon involves a dramatic explosion as one star interacts with another nearby star, a recurring event during the long, slow death of stars in a binary system.
The Blaze Star
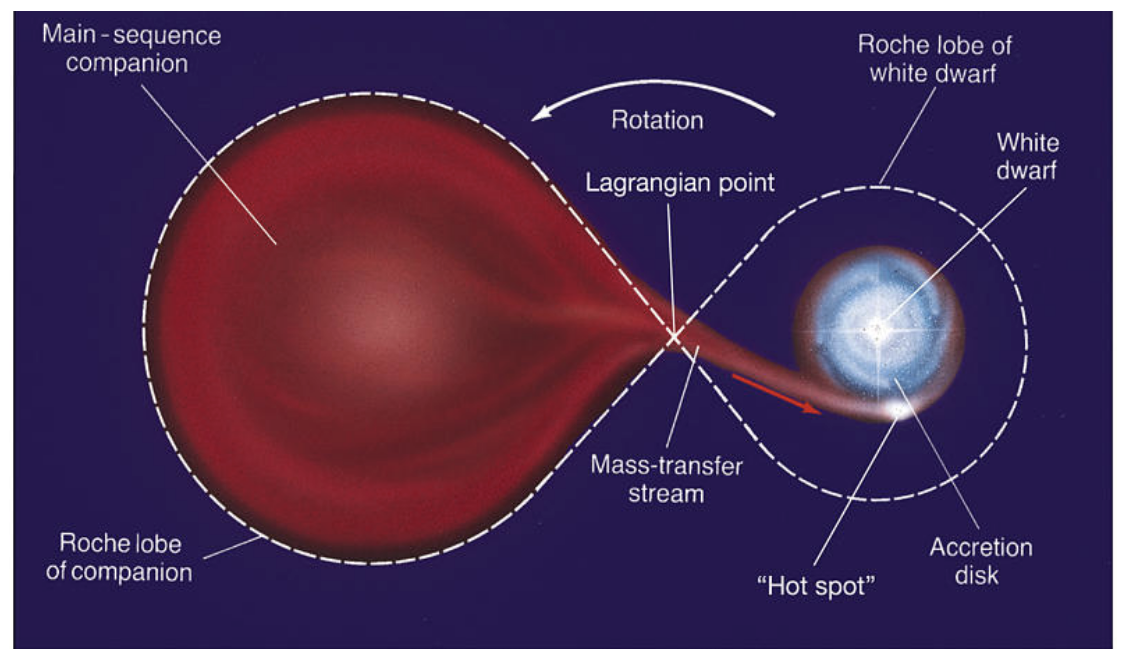
- The star system known as T Coronae Borealis, or "Blaze Star" (T CrB), consists of two stars: a white dwarf and a red giant.
- The white dwarf, a dense remnant of a once larger star, is about the size of Earth but with the mass of the Sun.
- Its neighbour, the red giant, is in its final stages of life and is being stripped of hydrogen by the gravitational pull of the white dwarf.
- This process leads to a tremendous buildup of pressure and heat, triggering the nova explosion.
Recurrent Novas
- T CrB experiences nova events roughly every 80 years, making it a "recurrent" nova.
- Historical records suggest prior eruptions were observed as far back as December 1787 and October 1217 AD.
Nova vs. Supernova
- A nova is not the same as a supernova.
- While a supernova is the final, destructive explosion of a star, a nova event does not destroy the white dwarf, allowing the process to repeat over time.
What Will the Nova Look Like?
- To the naked eye, the nova will appear as a new star in the sky.
- High-powered telescopes will reveal more detail, showcasing the brightly coloured luminosity of the nova.
- The explosion will increase T CrB's brightness dramatically, making it visible to the naked eye for several days.
How to Find T CrB?
- The T CrB system is located in the Northern Crown (Corona Borealis), a horseshoe-shaped curve of stars west of the Hercules constellation.
- To locate the Northern Crown, find the two brightest stars in the Northern Hemisphere: Arcturus and Vega.
- Tracing a line between these stars will lead you to the Northern Crown, where T CrB lies.
|
Red Giant and Dwarf Star
|