News Excerpt:
The Patna High Court nullified Bihar government's decision to raise caste-based reservations from 50% to 65% in educational institutions and government jobs, citing the need to balance merit and reparations.
More about News
- The Bihar assembly had unanimously passed bills to increase the reservation quotas based on Bihar Caste-based Survey 2022.
- The new rules raised the quotas for SCs to 20%, STs to 2%, EBCs to 25%, and OBCs to 18%, with a total of 65% reserved for these groups.
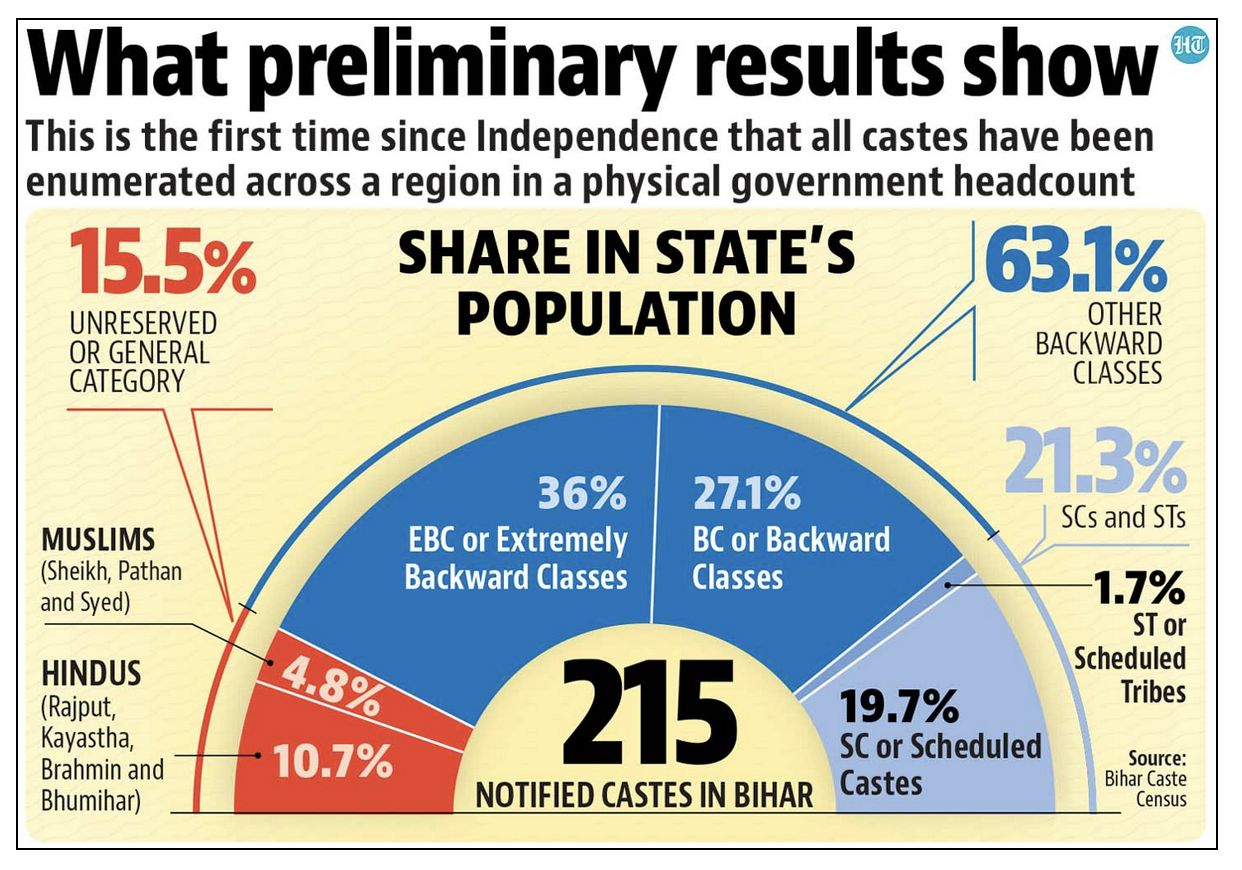
Bihar Caste-based Survey 2022:
- New Reservation rule is based on the caste based survey that had revealed that EBCs and OBCs together made up 63.13% of the state’s population while SCs were 19.65%, STs 1.68%, and upper castes 15.52%.
- Government decided to increase reservations for SCs, STs, EBCs, and OBCs after a caste survey indicated these groups made up 84% of the state’s population.
Court’s Observations:
- The Patna High Court noted the lack of scientific analysis and detailed study before implementing the quota increase.
- The court emphasized that while addressing historical injustices is crucial, it should not entirely overshadow merit.
- The court emphasized that it violated the Supreme Court’s 1992 Indira Sawhney judgment, which caps reservations at 50%.
- Stressed the importance of excluding the creamy layer within backward classes to ensure equitable distribution of benefits.
- The court declared this act unconstitutional as it violates equality provisions under Articles 14, 15, and 16.
- It was noted that backward communities were already sufficiently represented in public employment through existing reservations and merit.
State Government's plan
- The Bihar government plans to challenge the verdict in the Supreme Court after seeking further legal consultation.
Previous Example
- The court’s decision contrasts with Tamil Nadu’s law providing 69% reservations, which remains protected due to its inclusion in the Ninth Schedule of the Constitution.
- A Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court, in a 3:2 majority decision, upheld the validity of the 103rd Constitutional Amendment which provides 10% reservation in government jobs and educational institutions to the economically weaker sections.
- The Supreme court dismissed the argument that the 10% EWS quota would breach the ceiling limit of 50% on reservation.