News Excerpt:
The National Statistics Office (NSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation released CPI inflation data for May on June 12.
More about News:
- May is the fourth month in a row that food inflation has been over 8.5%.
- The inflation gap between urban and rural areas has been noticeable for the third month in a row. Rural households experienced a 5.3% price increase in May, while urban retail inflation was at 4.15%.
- In May, India's overall consumer price inflation slightly dropped to 4.75% from 4.83% in April, marking a one-year low.
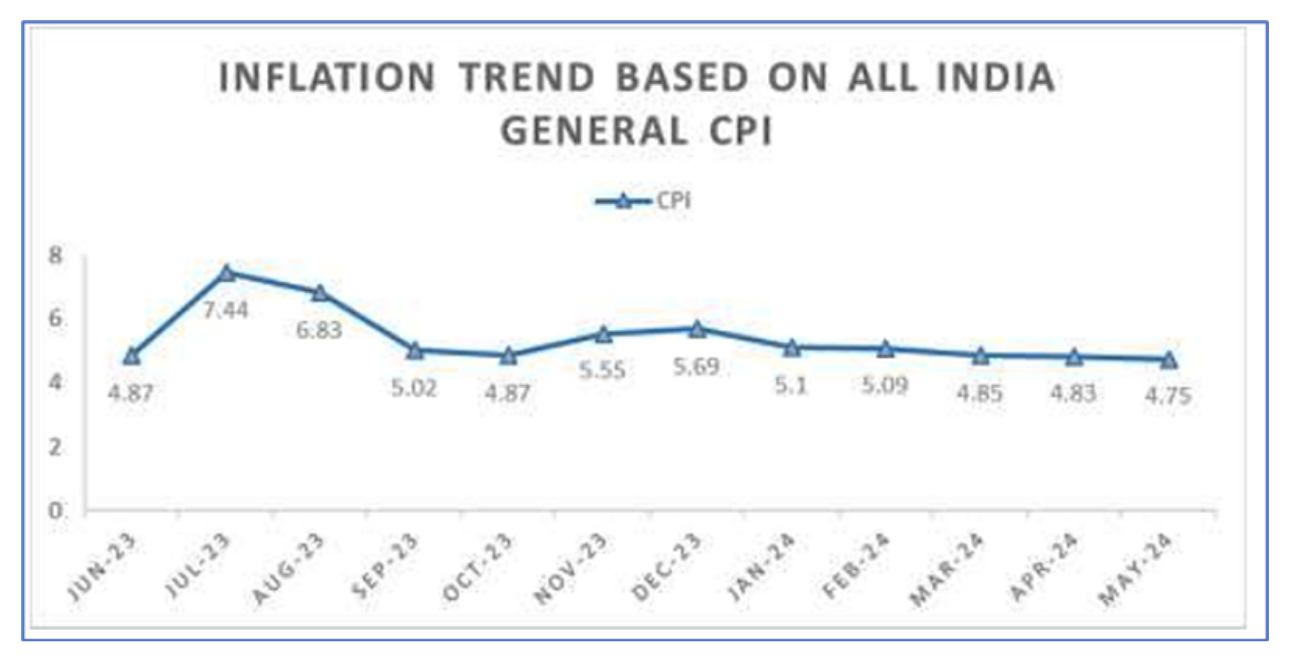
- However, food prices continued to rise, especially affecting urban households with an 8.83% increase in food inflation.
Inflation Overview
- Although the Consumer Price Index (CPI) is on a downward trend, frequent shocks in food prices have slowed down this process.
- Despite some easing, the prices of pulses and vegetables stayed high, especially during the summer.
- Fuel prices dropped mainly due to a cut in LPG prices in March.
- Core inflation, which excludes volatile items like food and fuel, has been decreasing for eleven months.
Concerns and Positive Signs
- The hot summer and low water levels could hurt the summer crops of vegetables and fruits.
- Global food prices are rising, and the cost of industrial metals has gone up significantly this year. These trends could increase production costs for businesses.
- On a positive note, a forecast of an above-normal monsoon could help the main (kharif) crop season.
- Wheat procurement is higher than last year, and stockpiles of wheat and rice are plentiful, which might ease food inflation, especially for cereals and pulses.
- The outlook for crude oil prices remains uncertain due to geopolitical issues.
Inflation Forecast by RBI
- Assuming a normal monsoon, The RBI projected CPI inflation for 2024-25 at 4.5%.
- Even though retail inflation has been below 6% since September 2023, it is still higher than the RBI target of 4%.
- The progress of the southwest monsoon is expected to influence food inflation over the next few months.
- A favorable base effect is expected to last until July 2024, which might help counter potential price increases.
- The RBI's decision to cut policy interest rates will likely depend on food inflation trends in the coming months.
|
Measurement of Inflation Wholesale Price Index (WPI)
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
Consumer Food Price Index (CFPI)
Core Inflation
|
|
The Monetary Policy Framework
|


