News Excerpt:
In a recent initiative, the Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC) has implemented the Shallow Aquifer Management (SAM) model on a pilot basis in Hyderabad, prioritizing water security for the future.
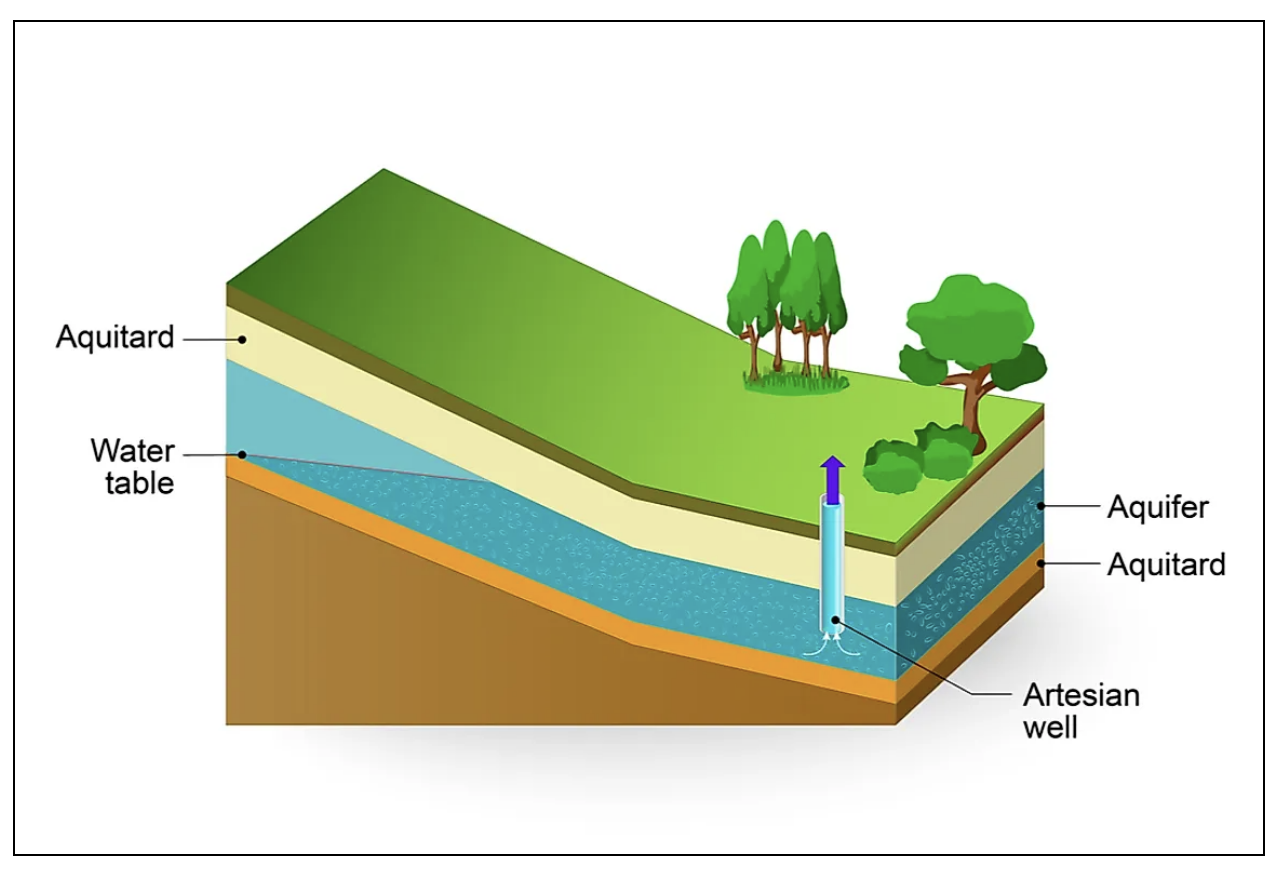
What is an Aquifer?
An aquifer is a body of porous rock or sediment saturated with groundwater. Groundwater enters an aquifer as precipitation seeps through the soil. It can move through the aquifer and resurface through springs and wells. It is of two types:
- Deep
- Shallow
What is Shallow Aquifer Management (SAM)?
- In 2022, the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) initiated a SAM pilot across 10 cities in nine states: Bengaluru (Karnataka), Chennai (Tamil Nadu), Dhanbad (Jharkhand), Gwalior (Madhya Pradesh), Hyderabad (Telangana), Jaipur (Rajasthan), Kolkata (West Bengal), Pune and Thane (Maharashtra), and Rajkot (Gujarat).
- The SAM pilot is coordinated by the National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA) and mentored by both the Advanced Center for Water Resources Development and Management (ACWADAM) in Pune and the Biome Environmental Trust in Bengaluru.
- Under SAM, the GHMC has identified five municipal parks this year.
How does it work:
- The project’s concept is to drill shallow water injection borewells to a depth of 100-120 feet and pump out water in the shallow aquifers.
- This is done so that the layers underneath get recharged whenever there is rainfall while collecting water from the surrounding watershed and channeling it through recharge pits. Thus, the underground layers are recharged, and the water table rises.
|
AMRUT Scheme:
|


