GS Paper III
News Excerpt:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation released the National Annual Progress Report on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), titled “Sustainable Development Goals-National Indicator Framework Progress Report 2024”.
- The report provides data-driven insights about India's progress and provides comprehensive information on Sustainable Development Goals monitoring.
About Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- In September 2015, during its 70th Session, the United Nations General Assembly adopted "Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development."
- This landmark document outlines 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and 169 associated targets, which took effect on January 1, 2016.
- The SDGs address global challenges such as poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, and the need for peace and justice.
- The 2030 Agenda emphasizes the importance of global partnerships and collaborative efforts involving governments, UN agencies, the private sector, civil society, and the public to ensure prosperity, peace, and a sustainable planet for current and future generations.

National Indicator Framework (NIF)
- India is dedicated to implementing the SDGs through nationally defined indicators aligned with its own priorities and needs.
- To integrate SDGs into national and sub-national policies and programs, NITI (National Institution for Transforming India) Aayog has aligned the SDGs with centrally sponsored programs across various Central Ministries and Departments.
- To support this effort, the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) developed a National Indicator Framework (NIF) for SDGs.
- Initially comprising 306 national indicators, the NIF was created through detailed consultations with relevant Ministries, UN Agencies, and other stakeholders.
- As of June 29, 2024, the NIF includes 290 national SDG indicators. MoSPI coordinates with Ministries and Departments to collect data on these indicators.
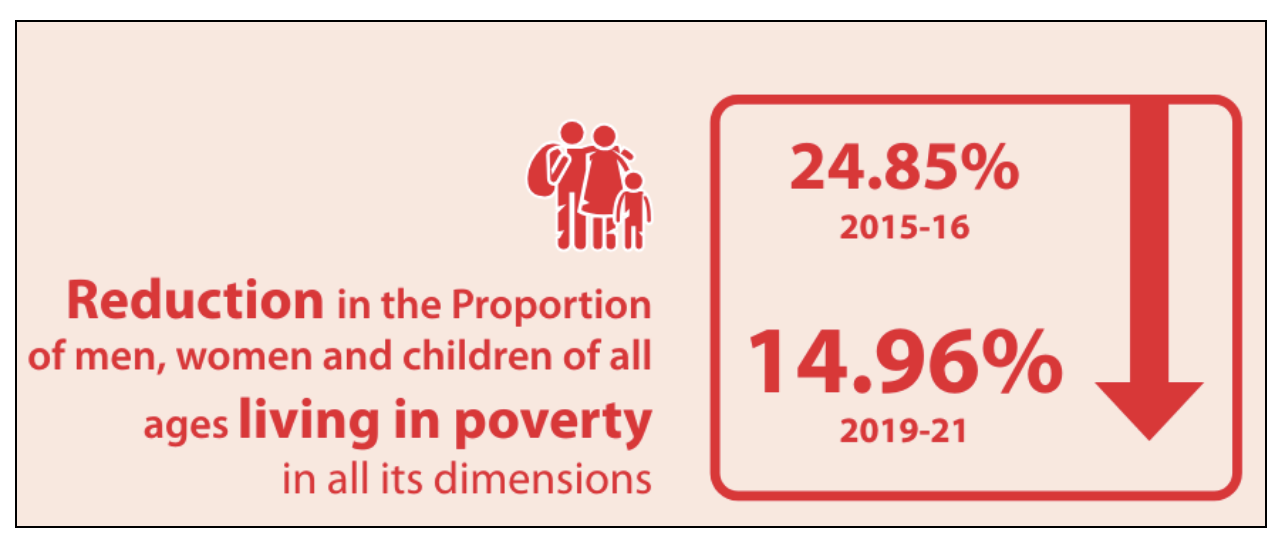
SDG 1: No Poverty
- It aims to eradicate poverty in all its forms worldwide.
- The Government of India has developed a comprehensive strategy to eliminate poverty in all its forms, recognizing its multidimensional nature.
- It has 18 national indicators identified to monitor these targets in India, and data is available for all indicators.
SDG 2: Zero Hunger
- It aims to eradicate hunger, achieve food security, improve nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture.
- In India, initiatives like the National Food Security Act of 2013 and the National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) have been pivotal.
- It has 19 national indicators identified to monitor these targets, and data is available for all indicators.

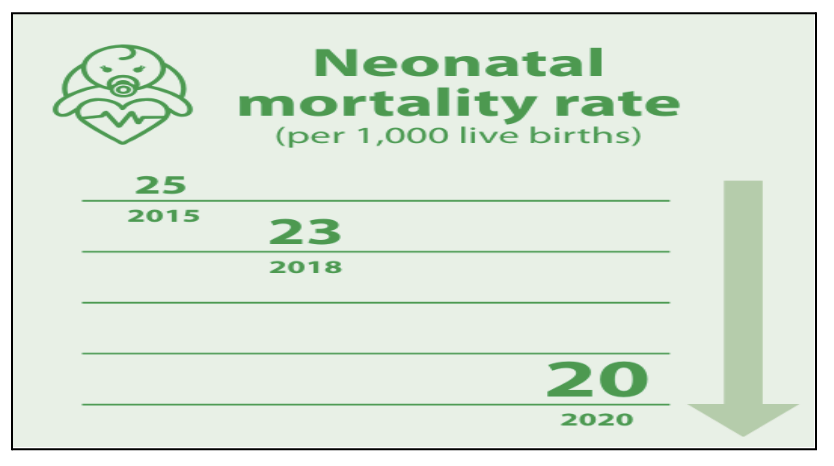
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-Being
- It aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for people of all ages.
- Key initiatives include the National Health Policy, Ayushman Bharat Yojana (the world’s largest health protection program), and Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana.
- It has 38 national indicators identified to monitor these targets, and data is available for all indicators.
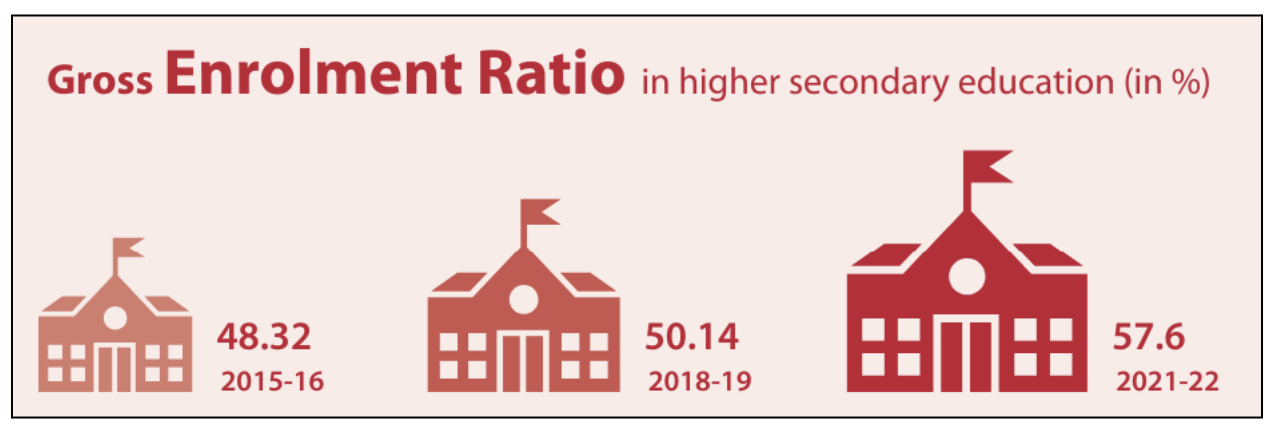
SDG 4: Quality Education
- It aims to provide students with the knowledge, skills, and competencies necessary for personal growth, future opportunities, and active participation in society.
- The Right to Education (RTE) Act guarantees free and compulsory education for every child between the ages of 6 and 14, establishing education as a fundamental right.
- At the national level, 19 indicators have been identified to monitor progress, with data available for 17 of them.
SDG 5: Gender Equality
- It aims to achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls, ensuring equal rights, opportunities, and treatment for all individuals, regardless of gender.
- The government has launched several social protection and financial inclusion programs aimed at increasing women's participation, such as Beti Bachao Beti Padhao, which has raised awareness and improved welfare services for girls, and the Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana, which provides maternity benefits to women.
- At the national level, 31 indicators have been identified to track progress, with data available for 28 indicators.
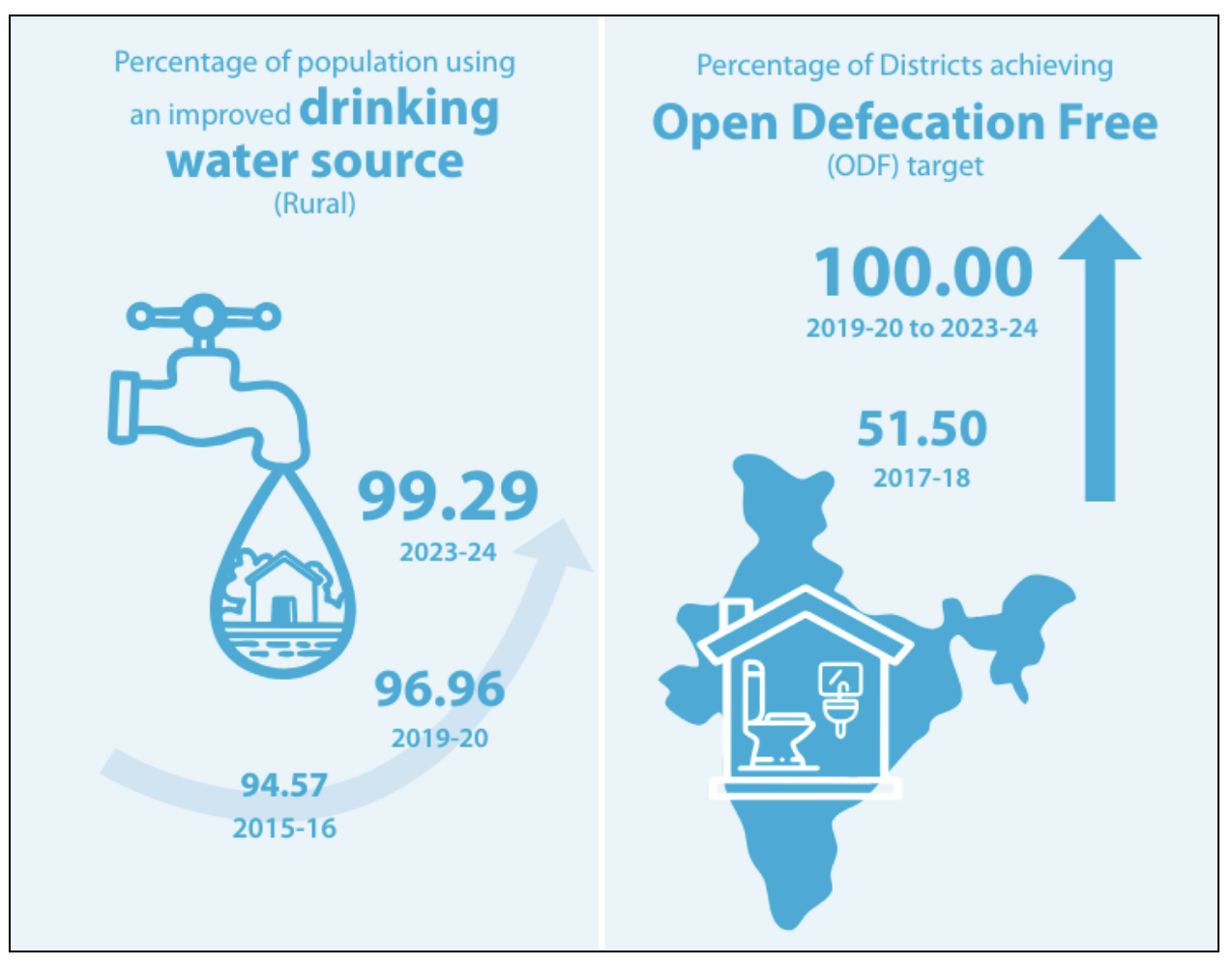
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- It aims to ensure the availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all.
- The Jal Jeevan Mission has been instrumental in developing water and sanitation infrastructure. Additionally, all districts in India have achieved Open Defecation Free (ODF) status under the Swachh Bharat Mission.
- At the national level, 13 indicators have been identified to monitor progress, with data available for all indicators.
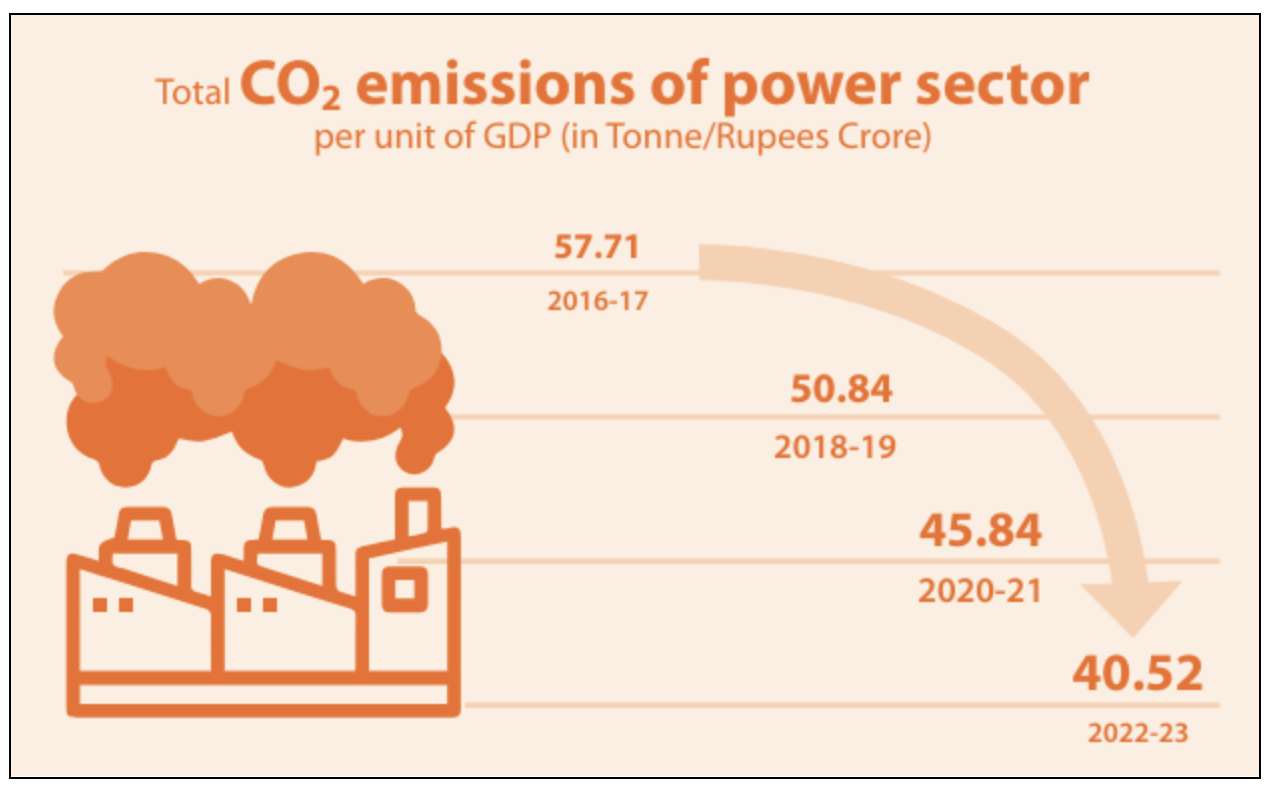
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- It aims to ensure the availability of energy sources that are both environmentally friendly and economically viable.
- The Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana - Saubhagya was launched to provide electricity access to all households, prioritizing renewable energy to reduce carbon emissions and air pollution.
- Additionally, the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana has effectively extended access to cooking gas to rural households, improving women’s health and reducing CO2 emissions.
- At the national level, 5 indicators have been identified to monitor progress, with data available for all indicators.

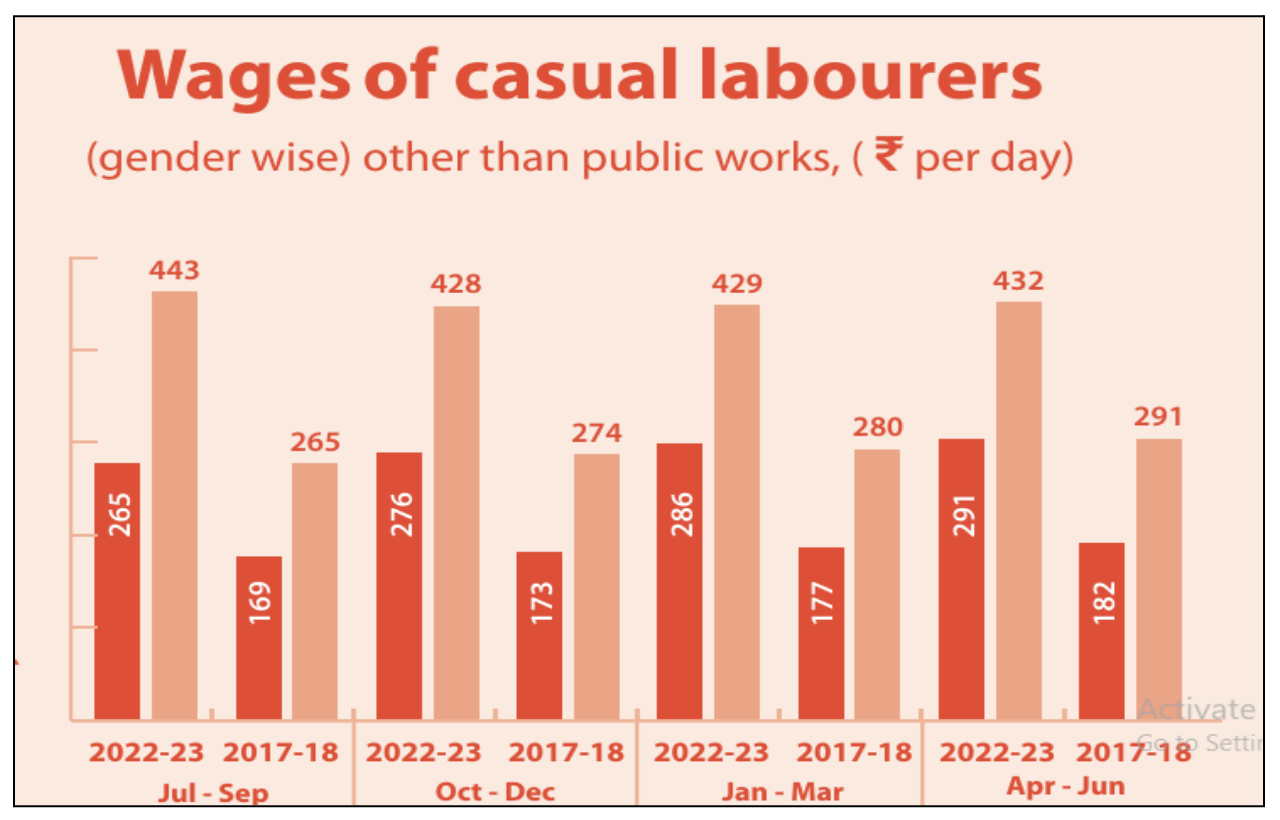
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- It aims to foster continuous, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth, along with ensuring full and productive employment and decent work for everyone.
- The government initiative, Startup India, aims to support Indian entrepreneurs, while the Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency (MUDRA) provides loans at low rates, benefiting MSMEs.
- At the national level, 26 indicators have been identified to monitor progress, with data available for 25 indicators.

SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- It focuses on building quality, reliable, sustainable, and resilient infrastructure that supports economic development and human well-being.
- Enhanced infrastructure and new initiatives such as the Dedicated Freight Corridor and various Industrial Corridors have played a pivotal role in fostering sustainable industrialization.
- At the national level, 16 indicators have been identified to monitor progress, with data available for all indicators.
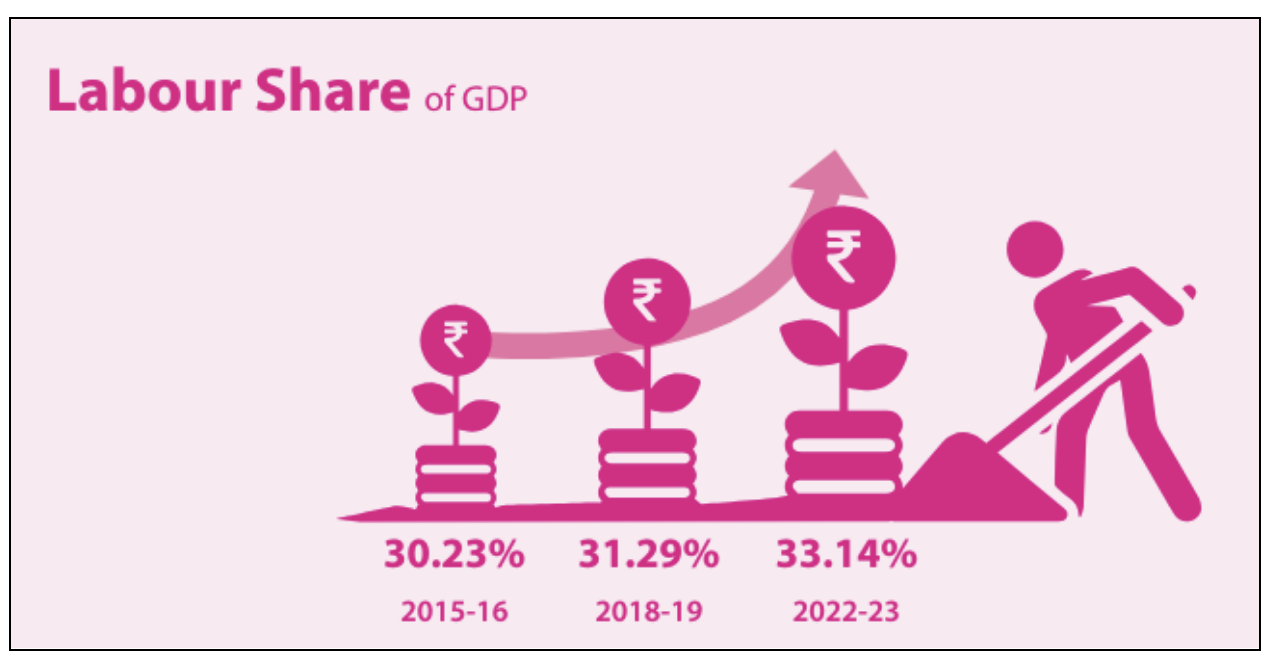
SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- It focuses on reducing inequality within and among nations, playing a critical role in promoting social justice, sustainable development, and human rights.
- Key initiatives include the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana and the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi.
- At the national level, 12 indicators have been identified to measure and monitor progress, with data available for all indicators.
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- It aims to create inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable cities and human settlements.
- The Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) focuses on establishing robust sewage networks and water supply infrastructure.
- The government also launched the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) to ensure affordable housing for all and the National Smart Cities Mission to develop smart cities across the country.
- At the national level, 13 indicators have been identified to measure and monitor progress, with data available for 10 indicators.

SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- It aims to ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns.
- India participates in international initiatives and agreements on sustainable consumption and production, including the 10 Years Framework of Programmes on sustainable consumption and production (10YFP).
- The government prioritizes renewable energy, organic agriculture, biofertilizers, and reduced emissions to ensure responsible consumption and production.
- At the national level, 14 indicators have been identified to measure and monitor progress, with data available for 10 indicators.

SDG 13: Climate Action
- It focuses on taking urgent measures to combat climate change and its effects.
- India’s National Action Plan for Climate Change (NAPCC) consists of eight missions aimed at mitigating and adapting to climate change while achieving developmental objectives with reduced emission intensity.
- In India 7 national indicators are available to monitor progress.

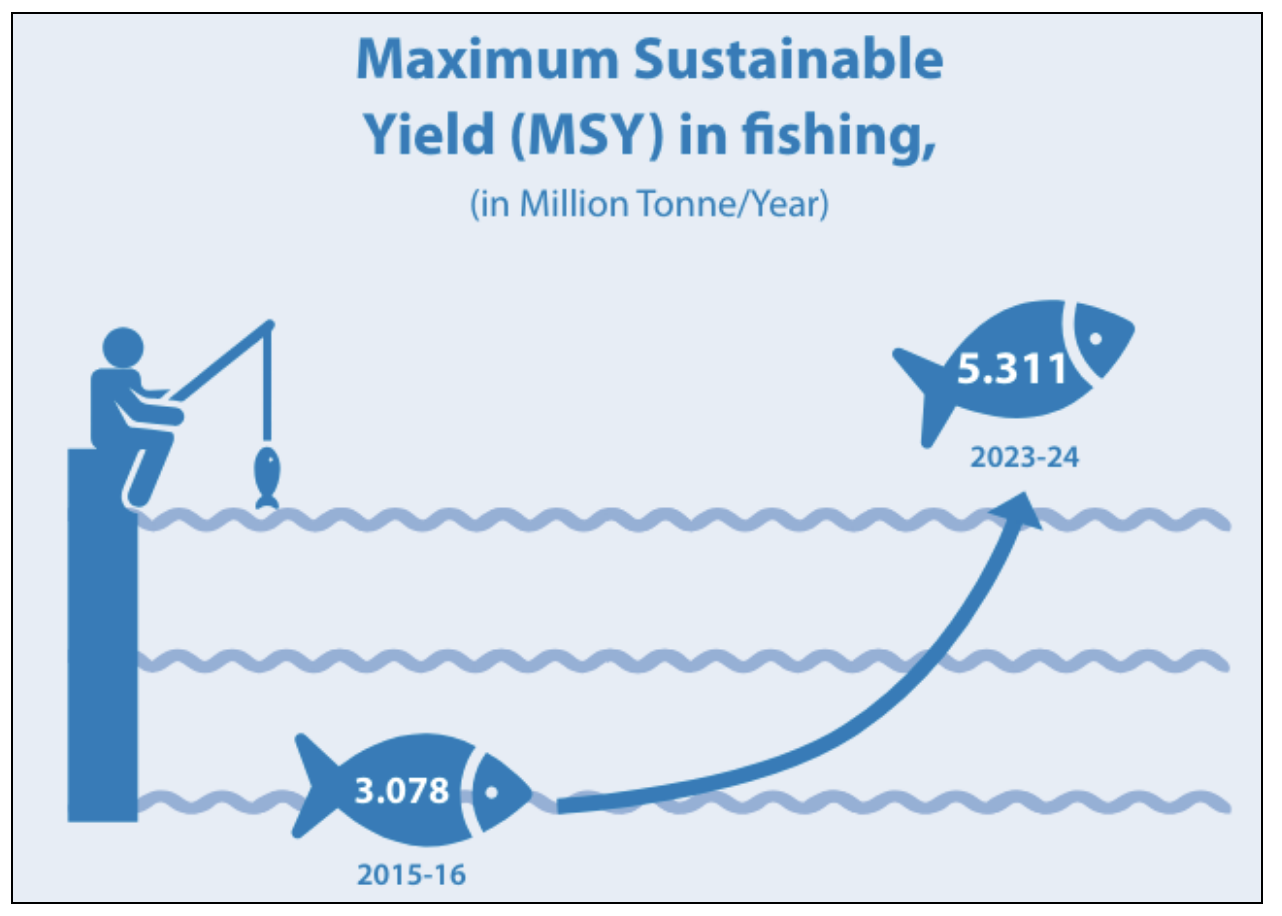
SDG 14: Life Below Water
- It aims to conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development.
- Initiatives have been undertaken to protect ecosystems like mangroves and coral reefs, contributing to sustainable fishing yields.
- In India 11 national indicators are available to monitor progress.
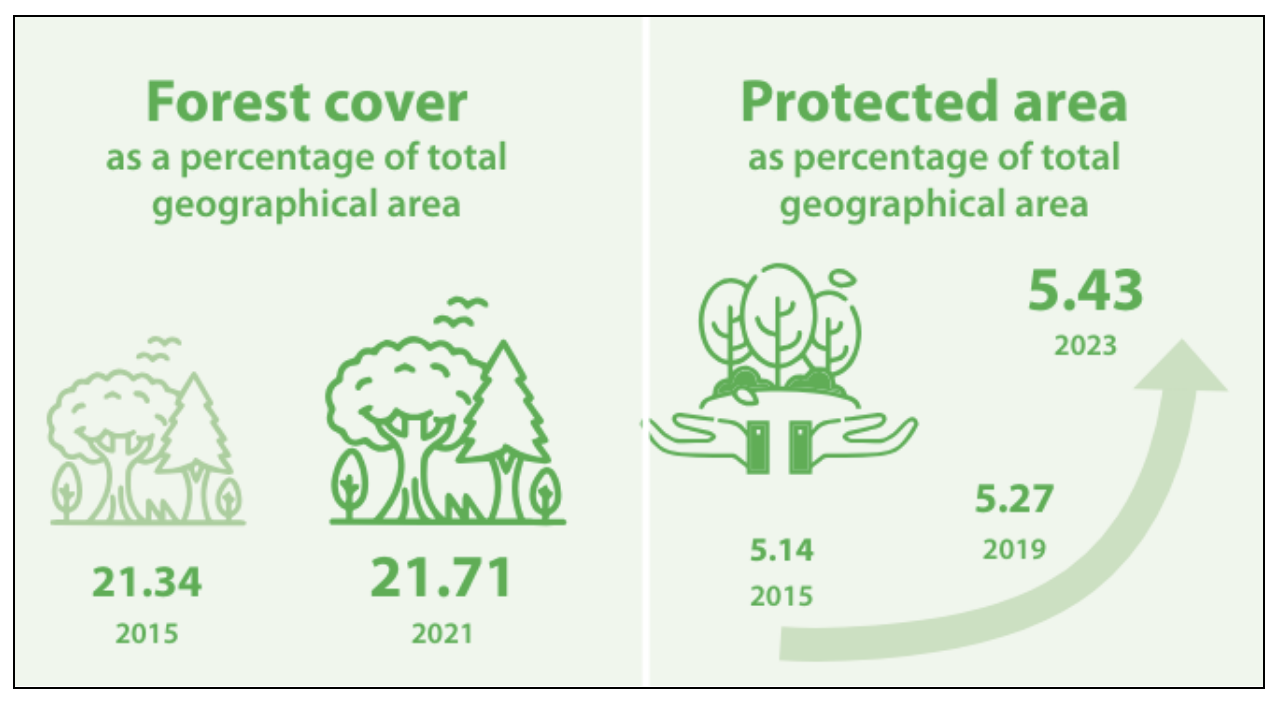
SDG 15: Life on Land
- It aims to protect, restore, and promote the sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, manage forests sustainably, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and biodiversity loss.
- In India 15 national indicators are available to monitor progress.

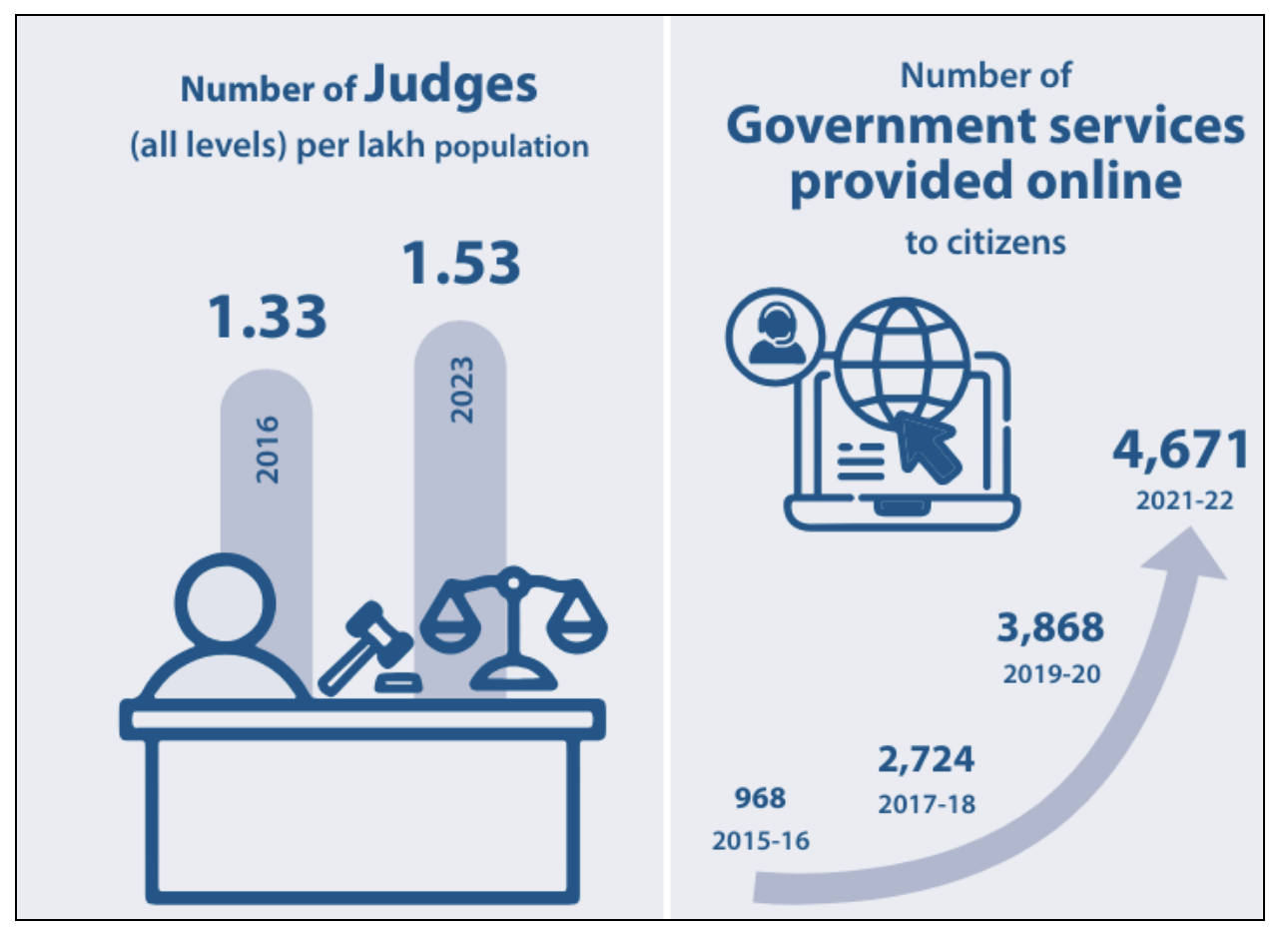
SDG 16: Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions
- It aims to promote peaceful and inclusive societies, provide access to justice for all, and build effective, accountable, and inclusive institutions.
- India’s Constitution embodies democracy, justice, liberty, and equality, supported by laws like the Right to Information Act, Lok Pal and Lok Ayukta Act, and Whistle Blowers Protection Act.
- In India 21 national indicators are available to monitor progress.
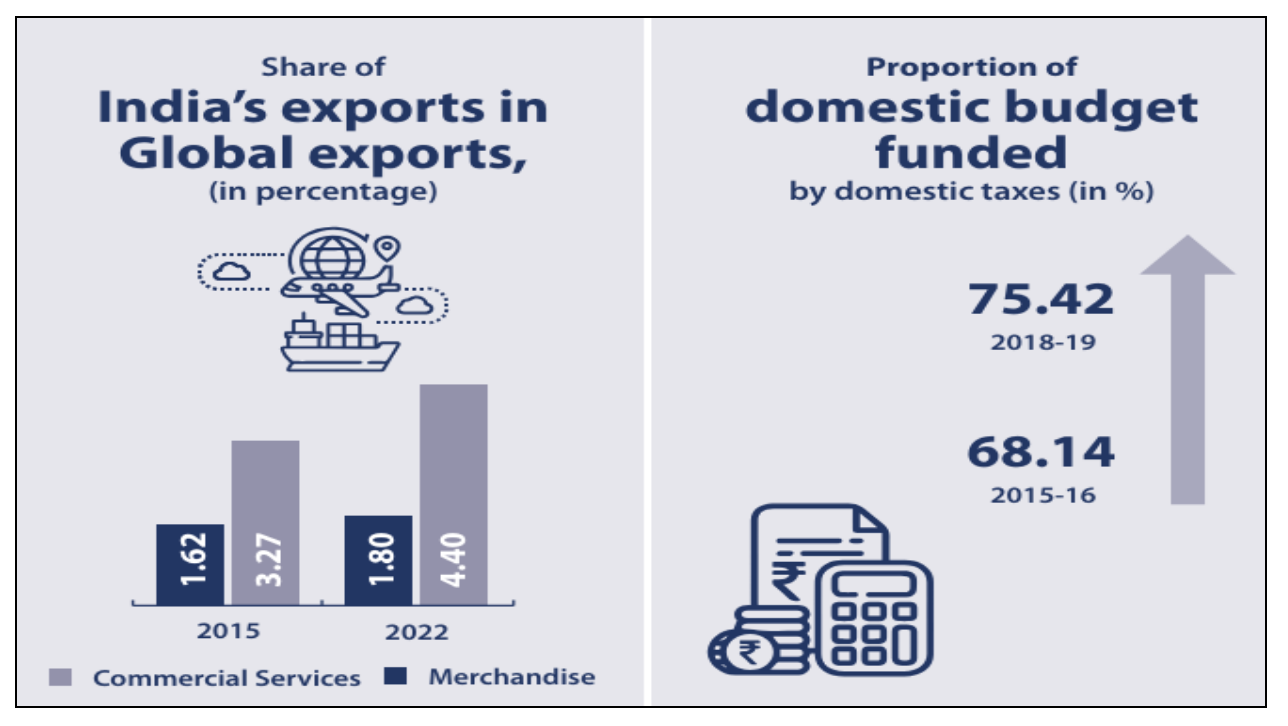
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- It aims to strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the Global Partnership for Sustainable Development.
- In India 12 national indicators are available to monitor progress.