News Excerpt:
The Ministry of Textiles is set to launch a pilot project in Bihar, specifically in Bhagalpur, a key castor-producing district, to explore the use of castor plants as an alternative to traditional mulberry silk production.
- The plan involves growing the insect Samia Ricini on castor leaves.
More About News
- Silkworms typically feed on mulberry leaves, but the ministry hopes to shift them to castor leaves, which have medicinal properties.
- The aim is to boost silk production and create more employment opportunities.
- The textile ministry's pilot project will start in Bhagalpur and may extend to other castor-producing districts in Bihar, including Purnea, Munger, Saran, Champaran, and Muzaffarpur.
- The success of this pilot could lead to a broader implementation across India, promoting castor as an alternative for silk production.
|
Castor Plant
|
Silk Varieties
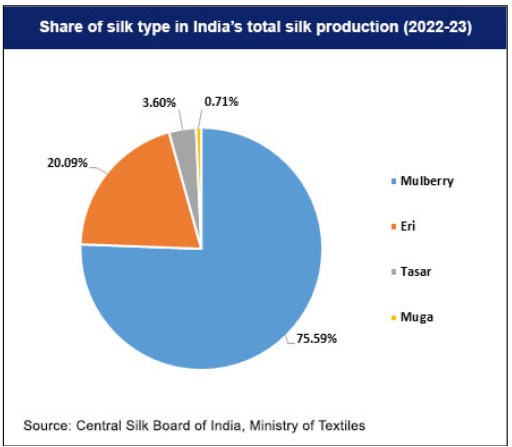
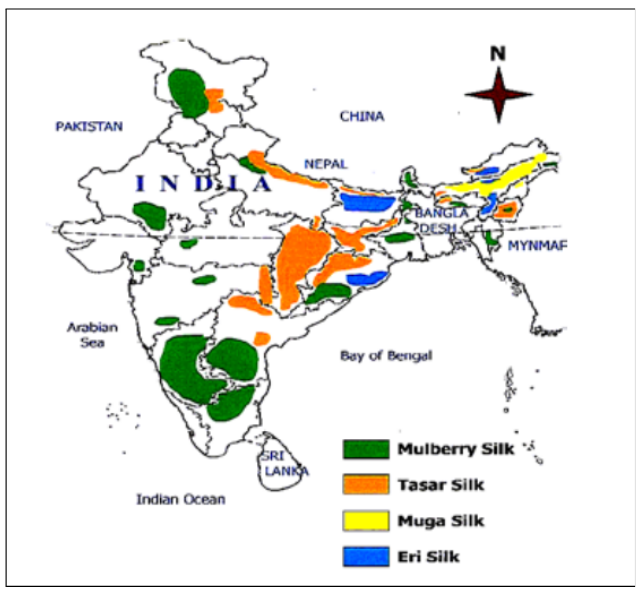
- The country produces four types of natural silks which are used in various textiles and accessories:
- Mulberry
- Eri
- Tasar
- Muga
- The silk produced from castor leaves, known as eri silk, is soft, warm, and durable, making it suitable for winter wear.
- Seeds of Castor plants are used in medicine and lubricants, and their stems, which are used for making thatched roofs.
Significance of Pilot Project
- Diversifying silk production to include eri silk could reduce dependence on mulberry silk and offer additional economic benefits to farmers due to the multiple uses of castor plants.
- The initiative also aims to increase silk production to reduce reliance on imports.
Silk Production in India
- India is the world's second-largest silk producer, with the sericulture industry employing around 9.2 million people in rural and semi-urban areas.
- India's silk imports have consistently exceeded exports, driven by high demand for high-quality silk products that domestic production cannot meet.
- India currently imports silk from Vietnam, China, Myanmar, Brazil, and Hong Kong, among others.
Challenges:
- President of the Silk Association of India (SAI), expressed skepticism, stating that there has not been a successful case of producing silk from castor or other leaves.
- Mulberry silk remains dominant due to its higher protein content, which is highly sought after.
- Land costs and the traditional use of castor as a border crop to protect main crops may deter farmers from diversifying their crops.


