News Excerpt:
UNESCO has recently approved the designation of 11 new biosphere reserves across 11 countries, marking a significant advancement in global efforts to preserve biodiversity and foster sustainable development.
More about the news:
- For the first time, Belgium and Gambia have been included, alongside the establishment of two transboundary biosphere reserves.
- These additions bring the total number of sites in the World Network of Biosphere Reserves to 759 across 136 countries, covering a combined area of 37,400 km², equivalent to the size of the Netherlands
- These new designations are a testament to UNESCO’s commitment to addressing the global biodiversity crisis and promoting sustainable development.

UNESCO Biosphere Reserve:
- A UNESCO Biosphere Reserve is a designated area that aims to balance biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
- These reserves are part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves, established under UNESCO's Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme.
- The reserves encompass terrestrial, marine, and coastal ecosystems.
- They are meant to function as living laboratories for sustainable development, showcasing innovative approaches to conserving biodiversity while fostering economic and human development.
Significance of Recognition:
- Conservation of Biodiversity: Biosphere reserves help protect various species and their habitats, contributing to global biodiversity conservation.
- Sustainable Development: They promote sustainable development practices, integrating conservation with socio-economic development.
- Research and Education: These reserves serve as sites for scientific research and education, helping to advance knowledge on sustainable living.
- Community Involvement: Local communities are involved in the management and development processes, ensuring that their needs and knowledge are integrated.
- Global Networking: Being part of a global network, biosphere reserves benefit from shared knowledge, resources, and collaborative efforts.
Biosphere reserves recognised are listed in the table below.
|
Biosphere Reserve |
Location |
Distinct Feature |
|
Kempen-Broek |
Belgium, Kingdom of the Netherlands |
Wetlands transformed into farmlands since the 19th century but the area retains remnants of its marshes, punctuated by ponds, open marshlands and bog forests. |
|
Darién Norte Chocoano |
Colombia |
Biodiversity bridge, significant archeological sites, home to Indigenous and Afro-Colombian people |
|
Madre de las Aguas |
Dominican Republic |
Diverse topography with critical habitats for endangered species such as Sparrowhawk (Buteo ridgwayi) |
|
Niumi |
Gambia |
Pristine mangrove forests, includes UNESCO World Heritage site Kunta Kinteh Island |
|
Colli Euganei |
Italy |
Volcanic hills, largest thermal basin in Europe, sustainable agriculture and ecotourism |
|
Julian Alps Transboundary |
Italy, Slovenia |
Alpine mountains, karst plateaux, diverse wildlife, extensive participatory planning |
|
Khar Us Lake |
Mongolia |
Diverse ecosystems, sustainable animal husbandry, heritage-based ecotourism |
|
yApayaos |
Philippines |
Apayao River watershed, Indigenous Cultural Communities, Lapat system(practice regulating the use of natural resources and protection of the environment.) |
|
Changnyeong |
Republic of Korea |
Includes Mount Hua Wang and Upo Wetland, diverse agriculture and conservation efforts |
|
Val d'Aran |
Spain |
North-facing valley, diverse climates, resilient rural development |
|
Irati |
Spain |
Second-largest beech forest in Europe, community-driven conservation |
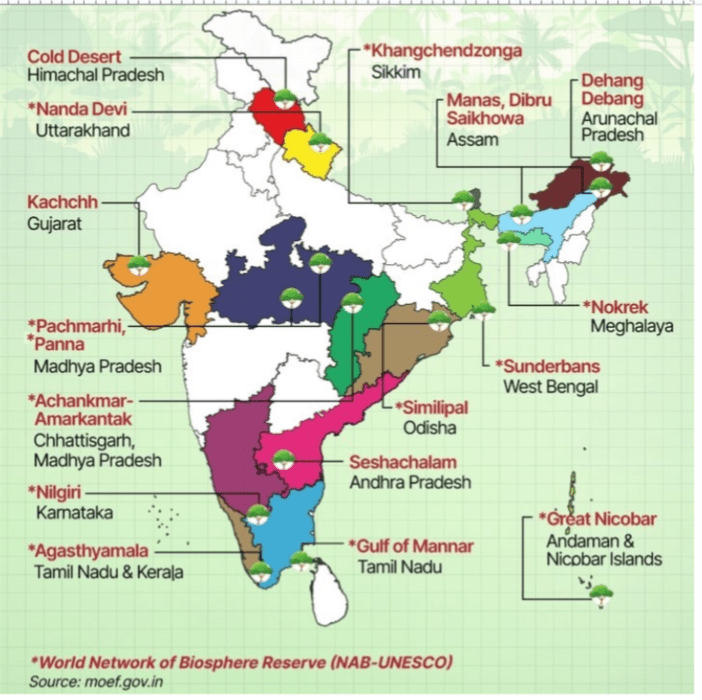
Biosphere reserves in India:
India has 18 Biosphere reserves with 12 biosphere reserves identified under UNESCO MAB Programme.