The IITs are over-committed, in crises
Relevance: GS II (Social Justice; Education)
- Mains: Indian Education institutions and associated issues; International and National interests.
- Prelims: World University Rankings 2024
Why in the News?
The IIT system is facing serious concerns about educational quality and faculty shortages. At the same time, some of them are building campuses abroad as part of India’s soft power efforts.

How do IITs stand as a significant source in building India’s Growth?
Any renowned institution is recognized through its objectives and principles. The following principles make IITs a significant contributor to India’s Growth :
- Its dedication towards excellence: The primary objective was to excel in technological education and research, aligning with global standards. It upholds a commitment to maintain higher academic standards and a reputation for excellence. IITs aim to contribute to India’s development by producing skilled professionals in emerging technology at its very root system.
- It does this by fostering and nurturing exceptional talent by practically imparting it in work fields of science and technology.
- Nurturing Innovation in National Developmental cause: IITs catalyze innovation, pushing the boundaries of research and technological advancements. By bridging the gap between academic theories and actual industrial practices, it helps to address real-world challenges.
- Its Global Reputation: IITs produce graduates and research outputs that make substantial contributions at both the national and global levels. Striving for global recognition, IITs sought to establish themselves as hubs of cutting-edge research and innovation.
- In the recent World University Rankings 2024, the remarkable position was achieved by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Bombay which ranked 149 in the list (first in the country), a significant jump from its previous ranking of 172.
What are the current challenges?
- Quality Concerns: New IITs struggle to match the standards of traditional institutes, with varying levels of prestige. The recent report on ‘Research performance of Indian Institute of Technology’ showed the quality of research carried out in old and new institutes is one of the main reasons that new IITs have not found space in any global ranking list.
- Faculty Shortage: According to the claim from the student's side, the teaching staff are usually visiting faculties. Severe shortage of experienced faculties in the IIT system is hindering the quality of education because top professors are unwilling to work in suburban areas.
- Overseas Campus Questions: Building an overseas campus as a part of the effort towards building soft power is of course a need. However, a careful look is needed to understand the present looming crises. When IIT-Madras opened a branch in Zanzibar and IIT Delhi planned to launch its programmes from Abu Dhabi (in 2024), it raised questions about the international expansion of IITs and its purpose.
- Standard Disparity: Unequal standards among IITs, with new institutions needing help to meet the excellence of traditional ones.
- Most importantly, the campus culture of old IITs is also different – Old IITs have cultural clubs and festivals that help in the overall development of students. Secondly, the old ones have more edge over the new ones in the form of dedication to robotics and journalism.
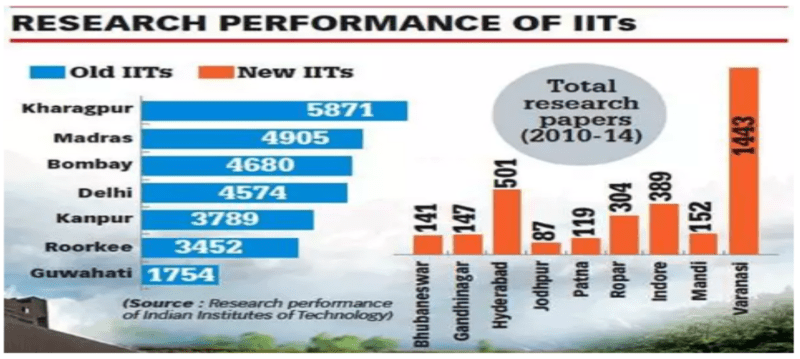
- Lack of Infrastructure: Lack of basic facilities, limited connectivity, under-construction college buildings and limited foreign collaboration are some of the reasons that new IITs are struggling for identity. Secondly, due to poor WiFi connectivity, labs are not fully equipped and the hostels are not enough to accommodate new incoming students.

Way Forward:
- Need for standardization of efforts: There is a need to prioritize quality over quantity in new IITs considering the expansion point of view. Implement measures to standardize the quality will eventually provide prestigious gain across all IITs. This will eventually cater for the over-expansion issue.
- Need to address resource demands: Considering the recent vacancy and faculty shortages in IITs, it is a must to attract and retain top talents through the best possible hiring process. Moving further, this issue doesn’t get solved. We need to update the skill development process at regular intervals by providing competitive salaries.
- Need for Evaluation of Foreign Ventures: Assessing the purpose and viability of overseas campuses is needed while ensuring high educational standards. There is a need to foster foreign collaborations, and industries to bridge the gap between theory and practice.
Though IITs are still on their way to establishing their uniqueness globally, we have some silver lining in this issue. We have an advantage over older IITs where the faculties have studied from the best universities of the world and can work as a guiding light from their golden experiences in our National Education Programmes and growth prospects.
Mains PYQs
- The quality of higher education in India requires major improvement to make it internationally competitive. Do you think that the entry of foreign educational institutions would help improve the quality of technical and higher education in the country? Discuss. (UPSC 2015)
- Comment on the challenges for inclusive growth which include careless and useless manpower in the Indian context. Suggest measures to be taken for facing these challenges. (UPSC 2016)
- Despite the consistent experience of high growth, India still goes with the lowest indicators of human development. Examine the issues that make balanced and inclusive development elusive. (UPSC 2019)
- Discuss the main objectives of Population Education and point out the measures to achieve them in India in detail. (UPSC 2021)
Prelims PYQ:
In India, the term “Public Key Infrastructure” is used in the context of (UPSC 2021)
a) Digital Security Infrastructure
b) Food Security Infrastructure
c) Health Care and Education Infrastructure
d) Telecommunication and transportation infrastructure.

