Massive Data Breach
| ‘Beware of the words "internal security," for they are the eternal cry of the oppressor’ - Voltaire |
Relevance: GS III (Science and Technology; Internal Security)
- Prelims: What are dark webs?
- Mains: Cyber Security and Money Laundering; Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal security.
Why in News?
In a massive data breach, details of over 81.5 crore citizens with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) are on sale.
|
Background:
|
What is the Dark web?
The dark web is the hidden collective of internet sites only accessible by a specialized web browser. It is used for keeping internet activity anonymous and private, which can be helpful in both legal and illegal applications.
State of Indian Cyber Security:
- India has averaged 1.3 million cyber attacks a year since 2020. Cyber attacks entail a financial cost.
- Last year, the Official Cybercrime Report by Cyber Security Ventures projected this cost globally at $8 trillion for 2023 and $10.5 trillion by 2025.
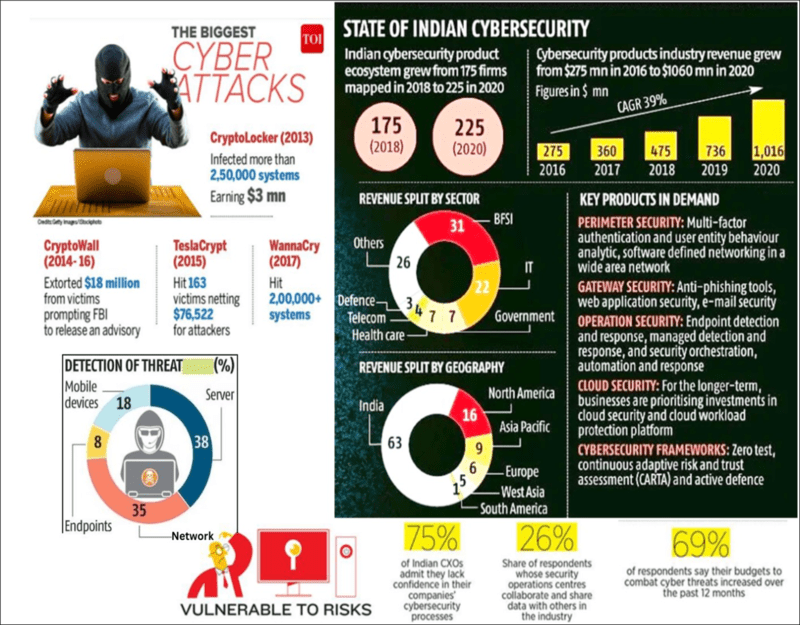
What are the security challenges that can occur due to data breaches?
- Target public portals through communication networks and disrupt the daily public system.
- Information Warfare: Use of information and communication technologies to manipulate, exploit, or disrupt the information and perception environment of the country promoting anti-national elements.
- Leakage of sensitive information like defence and security through attacks on communication networks.
- Destabilizing Critical Infrastructure like Nuclear power plants, power grids, Dams, and Share Market operations through cyber attacks.
- Penetrating Value Chain of production of communications network infrastructure for spying purposes.
- Economic Threats: Frauds, attacks on banking communication infrastructure, acquisition of critical data such as customer’s credit/debit card data, and financial theft to destabilize the economy.
Government Initiatives to protect Indian citizens from Data breach:
- National Security Directive on Telecommunication Sector 2021: It aims to classify telecom products and their sources under the 'trusted' and 'non-trusted' It will make its decision based on the approval of the National Security Committee on Telecom.
- Indigenization of technology: The government launched the 5G Non-Standalone (NSA) Core, indigenously designed and developed by C-DOT (Centre for Development of Telematics) at its pavilion in India Mobile Congress (IMC), in 2022.
- National Policy on Electronics 2019 (NPE 2019): Promotion for manufacturing critical infrastructure hardware components in India under a single indigenous policy. The development of a supply chain is essential for the manufacturing of electronic products with higher domestic value addition.
- The vision of National Policy is to position India as a global hub for Electronics System Design and Manufacturing (ESDM) by encouraging and driving capabilities in the country for developing core components, including chipsets, and creating an enabling environment for the industry to compete globally.
- Information Technology Act 2000: Under this act various network threats are considered.
- Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI): It regulates licensing of communication networks.
- National Digital Communications Policy in 2018: The Policy seeks to promote and protect fair competition across the communications and digital economy sector. The security of its citizens must be a prime consideration while participating in the global digital economy.
- Stay Safe Online Campaign: During India’s presidency of G20, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) is running a campaign titled ‘Stay Safe Online’ aimed at creating awareness among citizens including specially-abled persons to stay safe in an online world on the widespread use of social media platforms and rapid adoption of digital payments.
What are the Global Initiatives to avoid cyber crimes?
- Budapest Convention on Cybercrime: It is the first international treaty seeking to address Internet and computer crime by harmonizing national laws, improving investigative techniques, and increasing cooperation among nations. It came into force on 1st July 2004. India is not a signatory to this convention.
- Internet Governance Forum (IGF): The IGF is a global multi-stakeholder platform that facilitates the discussion of public policy issues pertaining to the Internet. It brings together all stakeholders i.e., government, private sector and civil society for the debate on Internet governance.
- UNGA Resolutions: At the 73rd session of the UN General Assembly (UNGA) on Human Rights, the resolution of the “right to privacy” in the digital age was adopted. The general assembly noted that every individual, especially children and women is more vulnerable to having their privacy violated.
- The United Nations General Assembly established two processes on the issues of security in the Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) environment.
- The Open-ended Working Group (OEWG) through resolution by Russia.
- The Group of Governmental Experts (GGE) through resolution by the USA.
- The United Nations General Assembly established two processes on the issues of security in the Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) environment.
Way Forward:
- Efficiency in regional Co-ordination and data dissemination: Formalize the coordination and prioritization of cyber security research and development activities; disseminate vulnerability advisories and threat warnings in a timely manner.
- Need for a Common Global Framework: Considering present geopolitical tensions, it has become the need of an hour to strategically solve this issue. It is needed as the current efforts are operating in silos. However, the help of a single apex body that ensures operational coordination amongst various agencies can solve the issue.
- Need for International Co-operation: To ensure tackling the rising issue with coordination, global cooperation is necessary through information sharing and strengthening joint efforts in cyber security research and development as most cyber attacks originate from beyond the borders.
- India can consider joining the Budapest Convention along with multilateral initiatives like QUAD.
- Reducing the gaps: Current requirement: It is important for the business and manufacturers or the respective government departments to find the gaps in their organizations address those gaps and create a layered security system, wherein security threat intelligence sharing is happening between different layers.
BEYOND EDITORIAL:
Key differences between various drafts of the Data Protection Law:
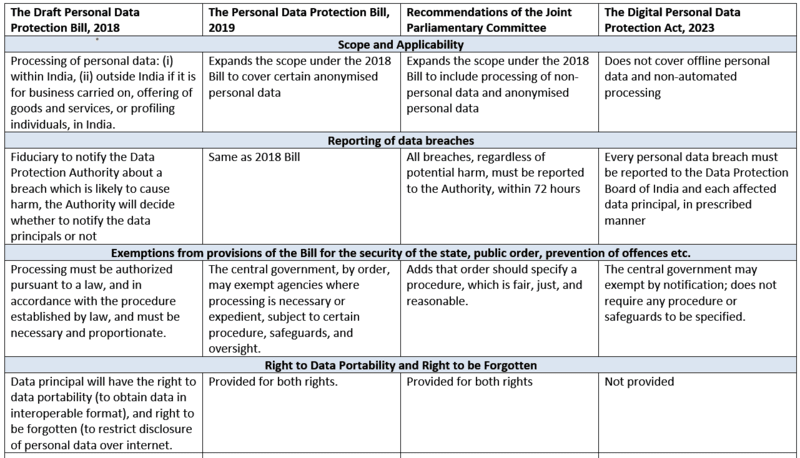
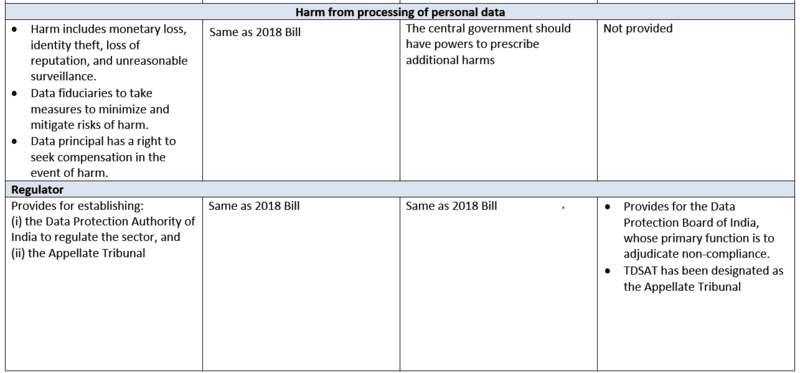
|
PYQs
|


